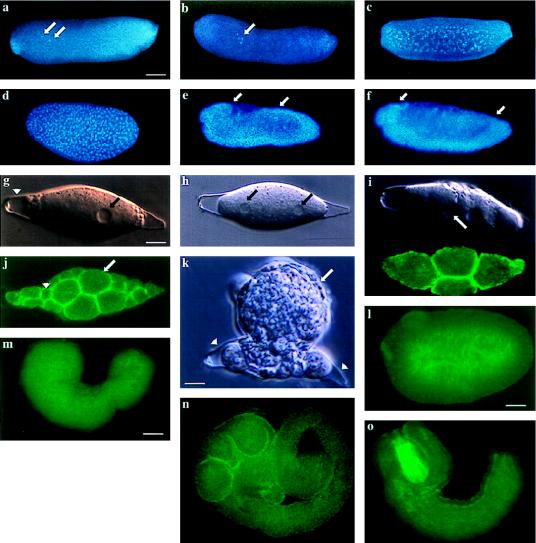
Figure 2.
Embryogenesis of B. hebetor and A. ervi. Confocal, fluorescent, and Nomarski images of embryonic development. (a) After oviposition the B. hebetor egg has a clear polarity corresponding to the dorsal-ventral and anterior-posterior embryonic axes. Embryonic nuclei (arrows) divide without cytokinesis. (b, c) During the first few syncytial cleavages nuclei remain in the yolk (arrow). (d) After the tenth cleavage nuclei migrate to the periphery of the egg where they undergo two additional division cycles in the syncytium before finally forming a cellular blastoderm (39). (e) The embryo then undergoes germband extension (anterior and posterior limits of the embryo marked by the arrows in e and f). (f) This is followed by germband retraction and segmentation. (g) After oviposition, the A. ervi egg is lemon-shaped and does not exhibit any axial polarity (nucleus marked by an arrow(s) in g and h and chorion by arrowhead). (h) The first nuclear division proceeds in a syncytium, without cytoplasmic cleavage. (i) The second cleavage results in formation of four nuclei that become separated by cell membranes (Upper, a single focal plane with two blastomeres, the cell membrane is marked by an arrow; Lower, the same stage embryo, phalloidin staining demarcates the cell cortex underlying the cell membranes in all four blastomeres). (j) The embryo undergoes cleavage to form large (which form the future extraembryonic membrane, arrow) and small blastomeres (which form the embryo proper, arrowhead). (k) The extraembryonic membrane surrounds the embryonic cells (arrow) and the embryo ruptures from the chorion (arrowhead). (l–o) The embryonic primordium remains surrounded by the extraembryonic membrane and initiates morphogenesis in the host’s haemocoel. (l) Embryonic primordium. (m) The embryo undergoes germband extension by posterior growth. (n) Fully extended germband stage whereby the embryo assumes a coiled shape. (o) This is followed by condensation and segmentation of the embryo. (l–o) The extraembryonic membrane was removed. Bars = 80 μm (a–f and m–o); 7 μm (g–k); 50 μm (l).