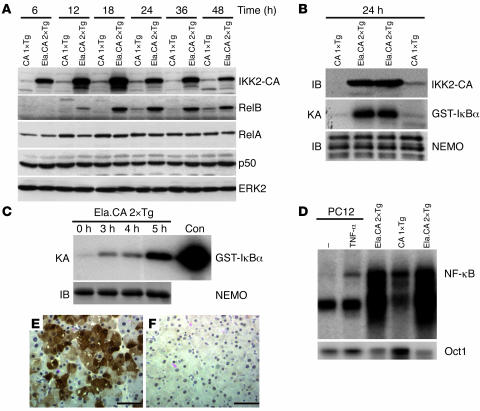
Figure 3. Expression and downstream signaling of IKK2-CA in transgenic mice.
(A) Immunoblot of pancreatic extracts demonstrated overexpression of IKK2-CA in double-transgenic Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice (Ela.CA 2×Tg) compared with single-transgenic IKK2-CA control mice (CA 1×Tg) between 6 and 48 hours after Dox injection. RelB expression was upregulated from 12 to 48 hours after Dox injection in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice, while RelA, p50, and ERK2 expression was unaffected. (B) Assay of kinase activity suggested activation of the kinase complex in pancreatic extracts from Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice 24 hours after Dox. NEMO immunoblot (IB) confirmed equal precipitation of the IKK complex in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA and single-transgenic IKK2-CA extracts. (C) In vitro treatment of isolated acini with Dox results in rapid and strong induction of IKK kinase activity, NEMO immunoblot served as control for the equal precipitation. Recombinant IKK served as a positive control (Con). (D) EMSA of nuclear extracts of isolated acini from Dox-treated mice (18 hours) demonstrates increased nuclear NF-κB binding in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice compared with controls. Protein extracts from TNF-α–treated pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells served as control for induced NF-κB activity. Oct1 DNA binding served as a control for the integrity of the nuclear extracts. (E and F) Immunohistochemical staining for IKK2 demonstrated patchy expression of the transgene in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice (E) and absent staining in the controls (F). Scale bars: 50 μm.