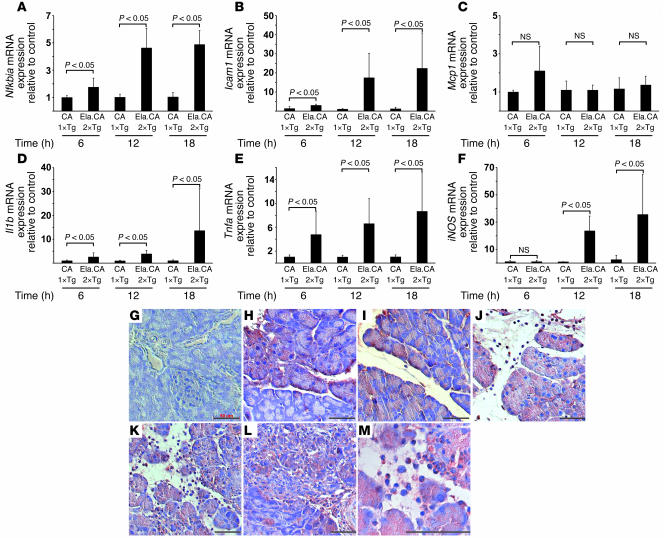
Figure 6. NF-κB–dependent target gene expression in the pancreata of IKK2-CA mice after Dox injection.
(A–F) Relative expression of target mRNA in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice, as assessed by quantitative RT-PCR, was normalized to endogenous cyclophilin expression and expressed as fold change over controls. (A) Nfkbia was upregulated up to 4-fold 6–18 hours after Dox injection in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice compared with controls. (B) Icam1 expression was increased, in particular at 12 hours after Dox injection, up to 20-fold that of controls. (C) Mcp1 mRNA was slightly increased 6 hours after Dox injection in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice. (D) Il1b was upregulated 18 hours after Dox injection. (E) Tnfa mRNA was induced in Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice at levels 7-fold those of controls 18 hours after Dox injection. (F) iNOS mRNA, a marker for invasion of immune cells, was increased at 12 and 18 hours after Dox injection. Values represent mean of 4–5 individual mice measured in duplicate. (G–M) Sections of single-transgenic IKK2-CA (G) and Ela.rtTA×IKK2-CA mice (H–M) were stained with anti–TNF-α. Patchy TNF-α expression was evident 6 hours after Dox treatment (H) and became more prominent after 12 hours (I) in the absence of invading leukocytes. Strong acinar staining and TNF-α–positive leukocytes were evident 18 (J) and 48 (K and M) hours after Dox injection. (L) Acinar TNF-α staining decreased 96 hours after Dox injection. Scale bars: 50 μm.