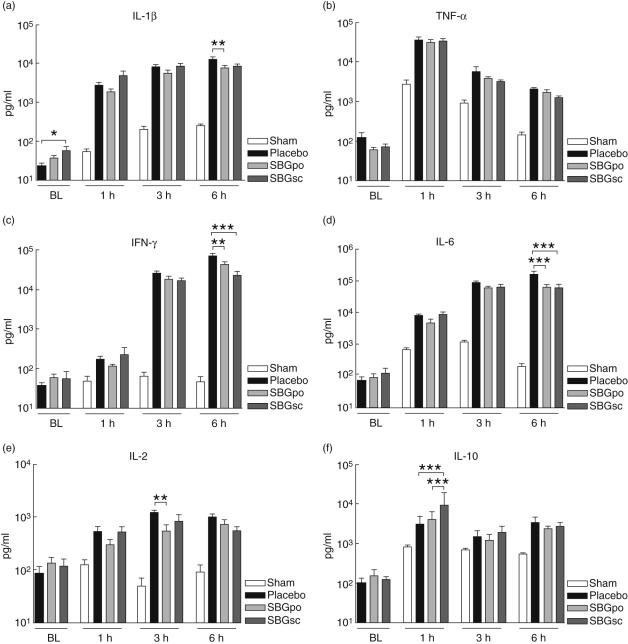
Fig. 5.
Effect of soluble Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived β-1,3/1,6-glucan (SBG) administration on plasma cytokine levels. Rats were pretreated with SBG or placebo and underwent surgery as described. Blood samples were collected from the cannulated carotid artery prior to administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or vehicle, BL, and 1, 3 and 6 h after infusion. Plasma levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1-α, IL-2, and IL-10 were analysed using a multiplex bead-array assay. Samples collected prior to LPS injection included SBGpo (n = 13), SBGsc (n = 10) and placebo (n = 14) experimental groups. Samples collected 1, 3 and 6 h after LPS challenge included SBGpo (n = 8), SBGsc (n = 8) and placebo (n = 8) experimental groups. No statistically significant differences were observed between the animals receiving vehicle (sham n = 20), regardless of SBG or placebo pretreatment (SBGpo n = 5, SBGsc n = 5 and placebo n = 10) (data not shown), thus the data were combined to one sham group. Data are presented as mean ± s. e.m. *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001 as determined by two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test.