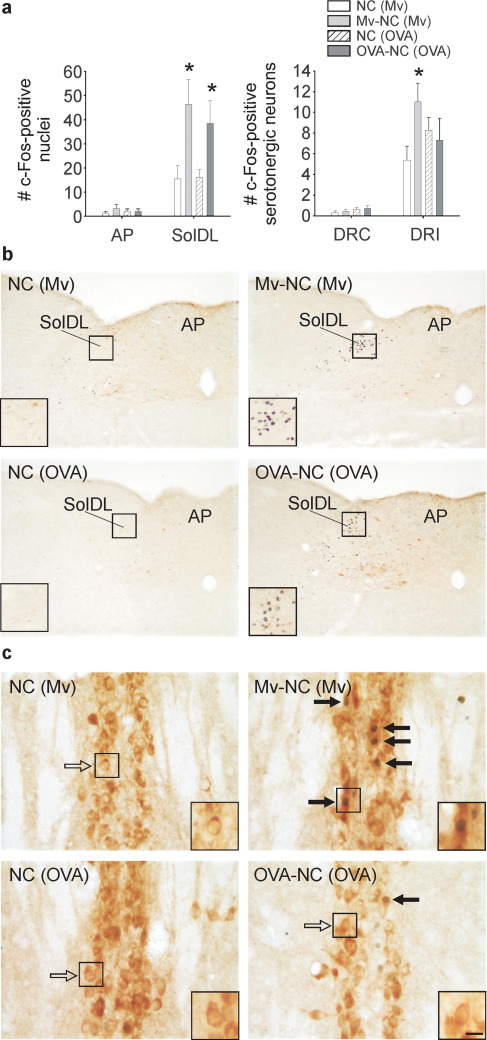
Fig. 2.
Both i.t. Mv-NC and i.t. OVA-NC induced c-Fos expression in the nTS but only Mv-NC increased c-Fos expression in DRI serotonergic neurons. Immunostained products are the same as in Fig. 1. (a) Bar graphs illustrate the mean number (±S.E.M.) of c-Fos-ir nuclei in the AP and SolDL (left) and c-Fos-ir/tryptophan hydroxylase-ir neurons in the DRC and DRI (right) in experiment 2. (b, c) Photomicrographs illustrate c-Fos responses to Mv-NC in M. vaccae–preimmunized mice or to OVA-NC in OVA/alum-preimmunized mice in the SolDL and AP (b) or the DRI (c). (⇒) c-Fos-immunonegative serotonergic neurons, ( ) c-Fos-immunopositive serotonergic neurons. Small black boxes indicate regions shown at higher magnification in insets. Scale bar=100 μm b; b (insets), 50 μm; c, 25 μm; c (insets) 12.5 μm. Abbreviations: (OVA), preimmunization with s.c. injections of OVA/alum; OVA-NC, i.t. challenge with OVA-NC. For additional abbreviations, see Fig. 1 legend. * P≤0.05, compared with the appropriate M. vaccae– or OVA/alum-preimmunized, vehicle-injected control group, Fisher’s protected LSD test.
) c-Fos-immunopositive serotonergic neurons. Small black boxes indicate regions shown at higher magnification in insets. Scale bar=100 μm b; b (insets), 50 μm; c, 25 μm; c (insets) 12.5 μm. Abbreviations: (OVA), preimmunization with s.c. injections of OVA/alum; OVA-NC, i.t. challenge with OVA-NC. For additional abbreviations, see Fig. 1 legend. * P≤0.05, compared with the appropriate M. vaccae– or OVA/alum-preimmunized, vehicle-injected control group, Fisher’s protected LSD test.