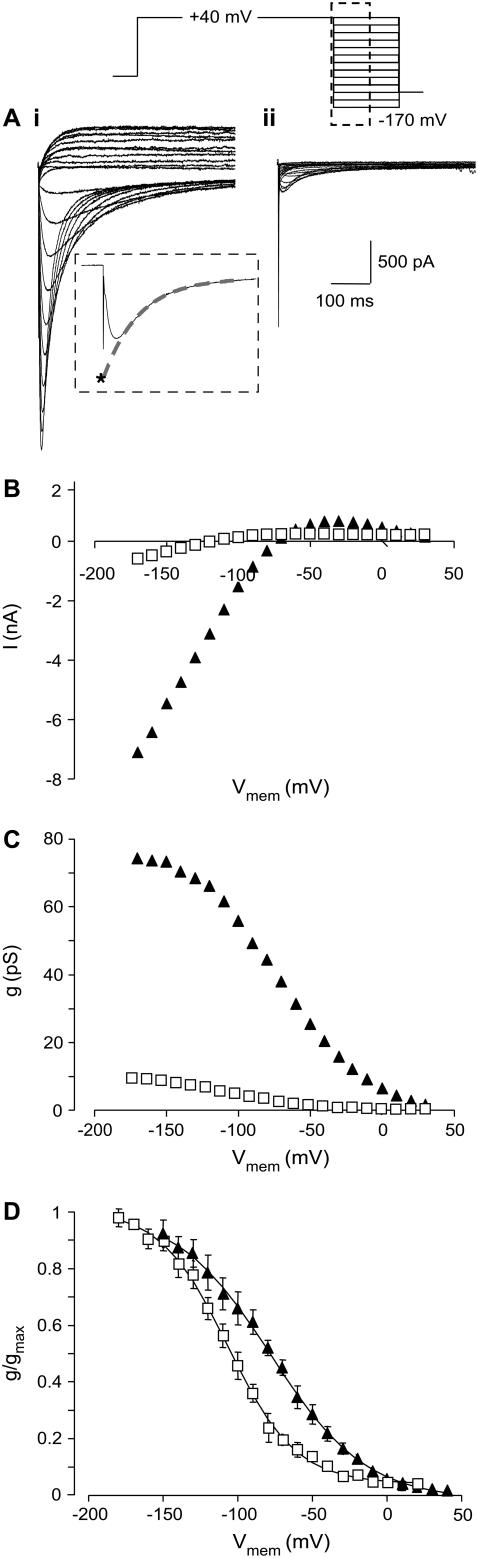
FIGURE 4.
Effect of 1 μM CnErg1 on voltage dependence of inactivation of hERG channels. (A) Typical example of current traces recorded in the absence (i) and presence (ii) of 1 μM CnErg1 during a 1 s activating pulse to +40 mV followed by a 500 ms step in the range +40 mV to −170 mV. Tails current recorded below −80 mV show the characteristic hooked appearance reflecting recovery from inactivation followed by deactivation. The inset shows a typical tail current recorded at −140 mV with the dashed shaded line indicating how peak current was corrected for deactivation. A single exponential was fitted to the timecourse of deactivation at each holding potential and extrapolated back to the origin of the voltage step (*). (B) Plots of corrected peak tail currents in the absence (▴) and presence (□) of 1 μM CnErg1 for the traces shown in panel A. (C) Data from panel B replotted as conductance versus voltage. (D) Summary of the effect of 1 μM CnErg1 on the voltage dependence of hERG inactivation. The lines of best fit are the Boltzmann function (see Materials and Methods) giving V0.5 for inactivation of −82.7 ± 5.7 mV (mean ± SE, n = 6) and −105.9 ± 2.9 mV (mean ± SE, n = 4) for control and 1 μM CnErg1, respectively.