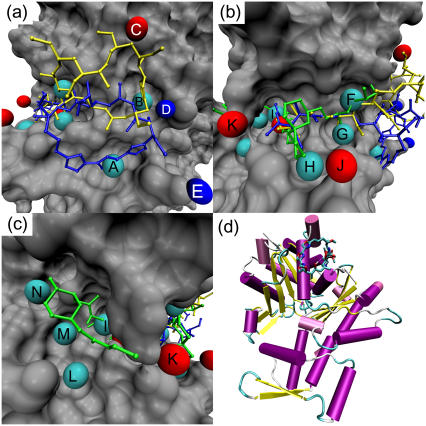
FIGURE 3.
Predicted important interactions at the gelsolin binding site of actin. Cyan spheres indicate hydrophobic interactions, red spheres hydrogen-bond acceptor interactions, and blue spheres hydrogen-bond donor interactions. (a) The hydrophobic pocket of actin. Kabiramide A (blue) and reidispongiolide A (yellow) are shown for reference. Key: A — hydrophobic interaction at Gly-23; B — hydrophobic interaction at Ser-141, Ala-144, Pro-332, Ser-338; C— hydrogen-bond acceptor interaction with Arg-147; D hydrogen-bond donor interaction with Glu-334; E — hydrogen-bond donor interaction with Asp-25. (b) The hydrophobic cleft of actin. Bistramide A (green), kabiramide A (blue), and reidispongiolide A (yellow) are shown for reference. Key: F — hydrophobic interaction with Arg-147 and Thr-148; G — hydrophobic interaction with Tyr-143 and Leu-346; H — hydrophobic interaction with Thr-351; I — hydrophobic interaction with Ile-135, Val-139, Tyr-169; J — hydrogen-bond acceptor interaction with Thr-351; K — hydrogen-bond acceptor interaction with Tyr-169. (c) The far end of the hydrophobic cleft of actin. Bistramide A is shown for reference. Key: L — hydrophobic interaction with Tyr-133 and Val-370; M — hydrophobic interaction with Val-134; N — hydrophobic interaction with Leu-110, Asn-111. (d) Cartoon representation of actin, with kabiramide C in its binding site at the top of the panel.