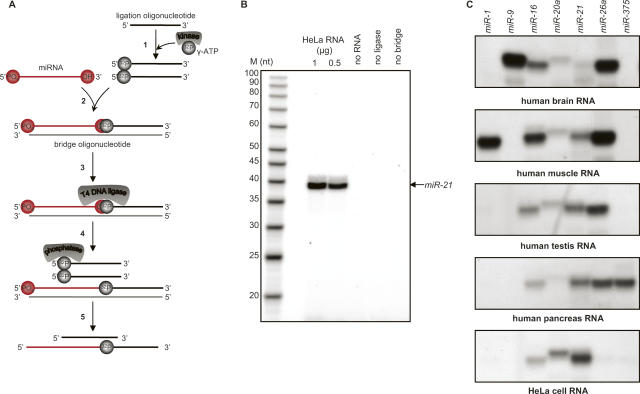
FIGURE 1.
Detection of miRNAs using splinted ligation. (A) Schematic depiction of the assay process. As described in the text, the assay involves: (1) Labeling of the ligation oligonucleotide; (2) concurrent annealing of the ligation oligonucleotide and miRNA to a bridge oligonucleotide; (3) linking of the ligation oligonucleotide to the miRNA by DNA ligase; (4) removal of labeled phosphate from unligated oligonucleotide; and (5) fractionation on a denaturing gel. (B) Assay reactions were performed with the indicated amounts of HeLa cell total RNA as described in Materials and Methods. Samples were separated on 12% urea polyacrylamide gels prior to autoradiography. Lanes designated “no ligase,” “no bridge,” and “no RNA” were complete reactions in which the specified components were replaced by water; 1 μg of total RNA was used in the no ligase, and no bridge reactions. Lane M, 5′-end-labeled oligodeoxynucleotides of the indicated sizes (USB). The arrow indicates the position of a synthetic miR21 RNA ligated and analyzed in parallel. (C) Detection of selected human miRNAs in different tissues by splinted ligation. Assays were carried out as described in Materials and Methods with the indicated miRNA-specific bridge oligodeoxynucleotides: a common labeled ligation oligonucleotide, and 500 ng of total RNA from the indicated tissues.