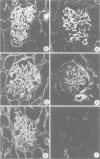
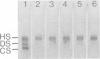
Abstract
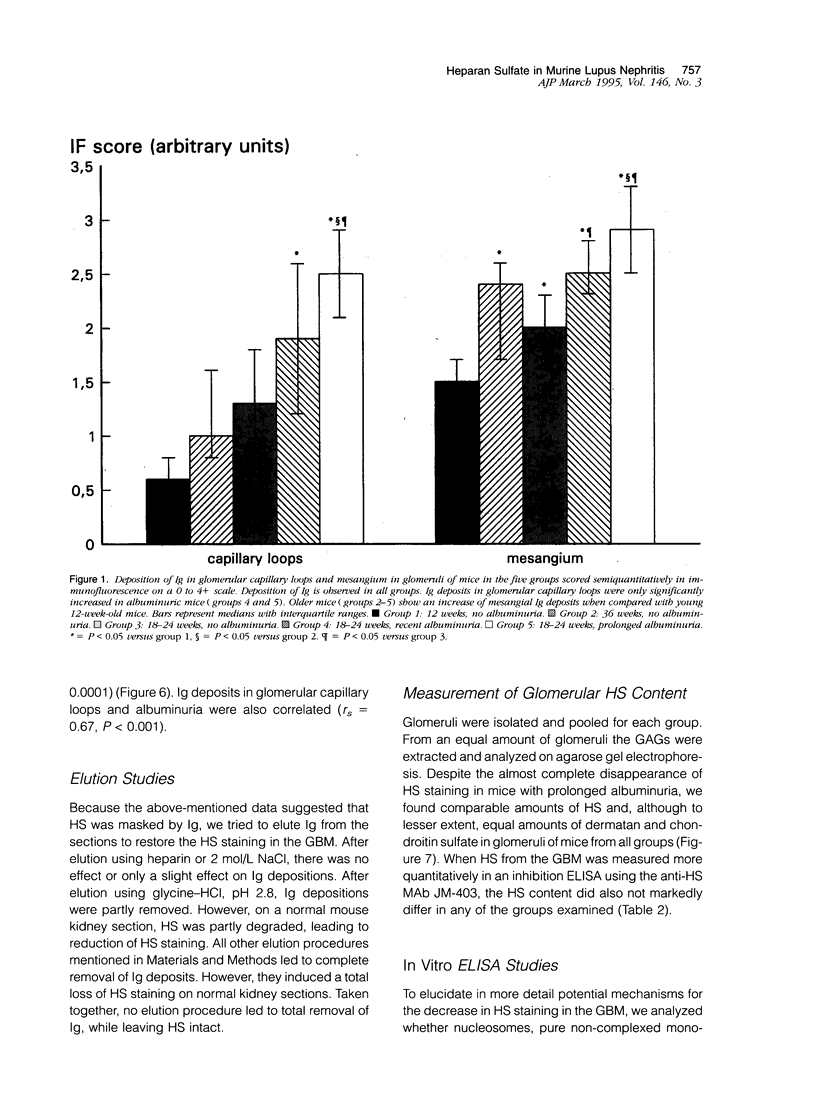
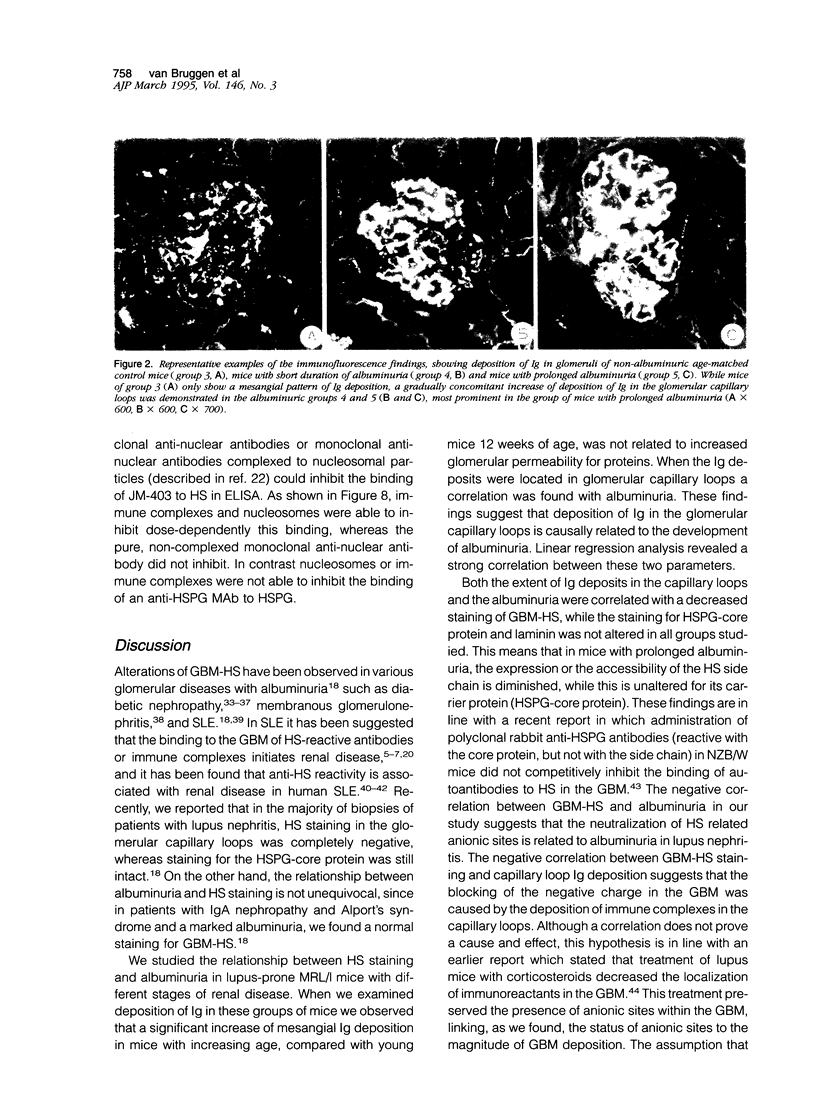
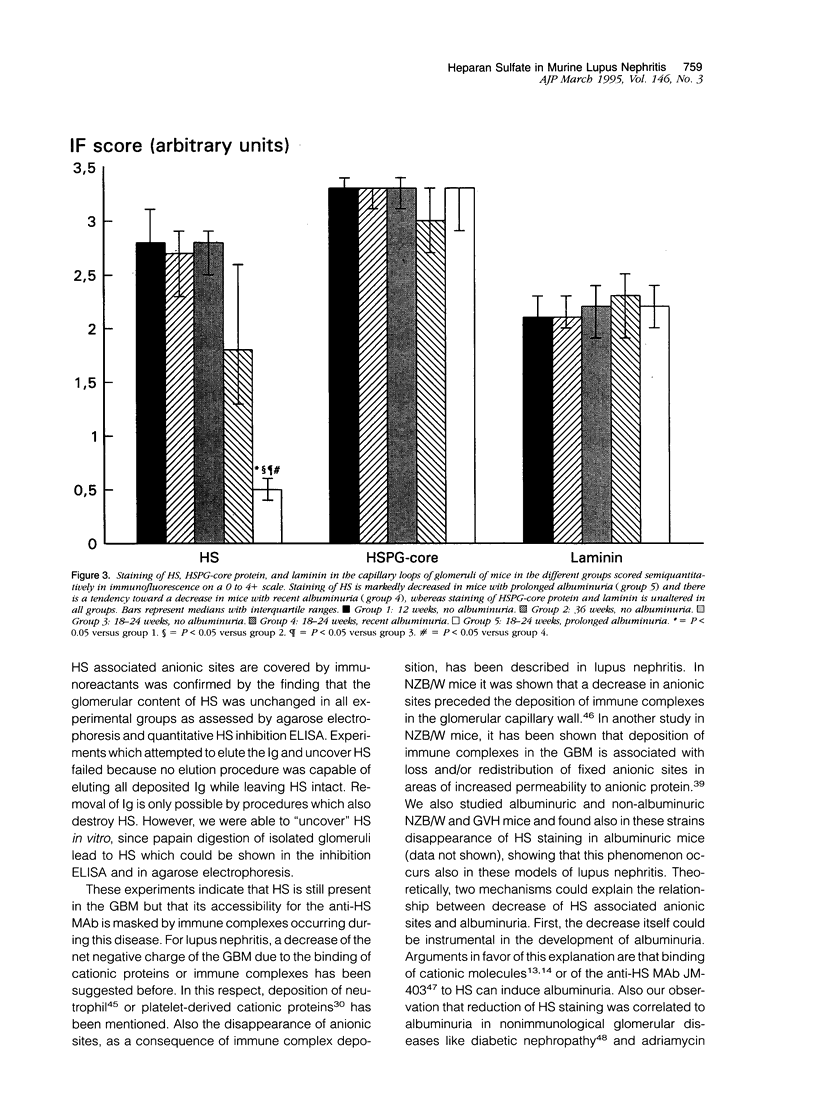
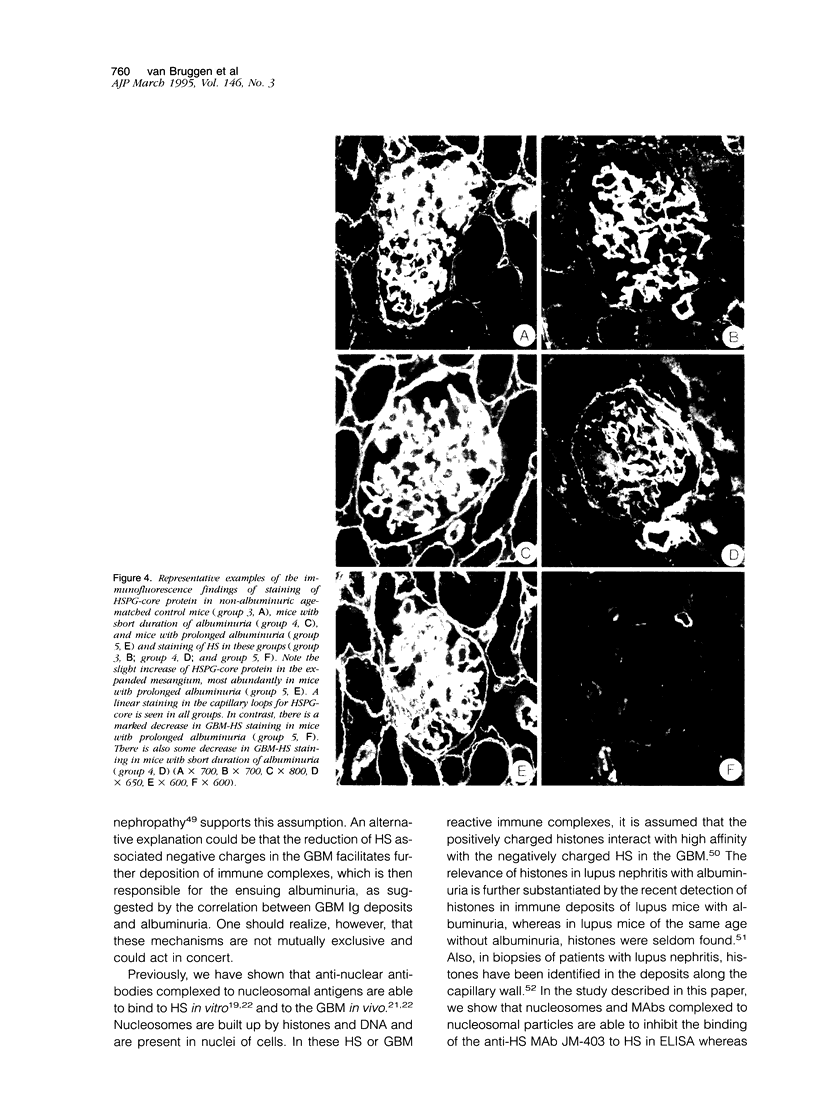
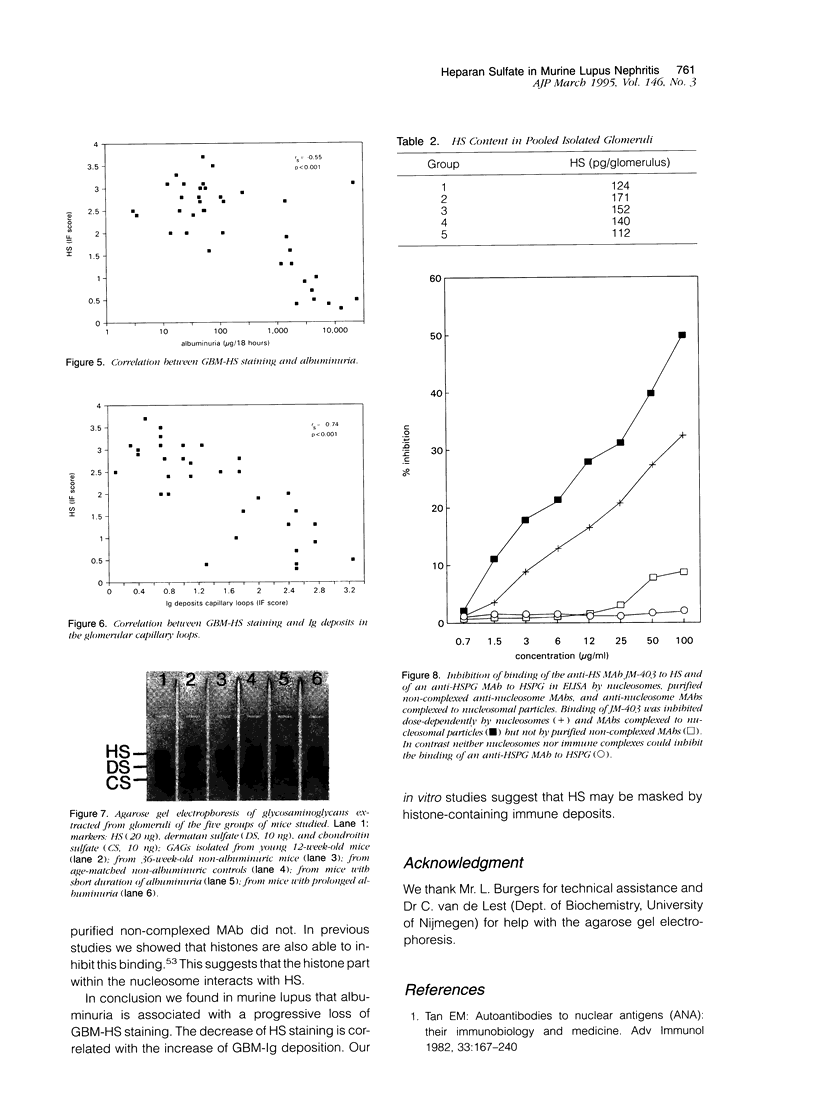
Recently we found in biopsies of human lupus nephritis a nearly complete loss of heparan sulfate (HS) staining in the glomerular basement membrane (GMB). To clarify the relationship between HS staining and albuminuria in lupus nephritis, we studied MRL/lpr mice with short (< 7 days) or prolonged duration of albuminuria (14-21 days) and compared these with mice of different ages without albuminuria. Kidney sections were stained for mouse immunoglobulin (Ig), HS, heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG)-core protein and laminin in immunofluorescence. In mice with prolonged albuminuria HS staining in the glomerular capillary loops had almost completely disappeared, whereas staining was unaltered in non-albuminuric mice (P = 0.001). In mice with short duration of albuminuria, there was a tendency toward a decrease of HS staining (P = 0.06). The expression of HSPG-core protein and other extra cellular matrix (ECM) components was unaltered in all groups. HS staining correlated inversely with albuminuria (rs = -0.55; P < 0.001) and with staining of Ig deposits in the capillary loops (rs = -0.74; P < 0.001). Despite the nearly complete loss of HS staining in the GBM in mice with prolonged albuminuria, there was no change in glomerular HS content as assessed by agarose electrophoresis and HS inhibition ELISA. We conclude that the development of albuminuria in MRL/lpr mice is accompanied by a loss of HS staining in the GBM, probably due to the masking of HS by deposits of Ig. In vitro studies revealed that autoantibodies complexed to nucleosomal antigens can inhibit the binding of the anti-HS monoclonal antibody to HS. Whether this also occurs in vivo remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assel E., Neumann K. H., Schurek H. J., Sonnenburg C., Stolte H. Glomerular albumin leakage and morphology after neutralization of polyanions. I. Albumin clearance and sieving coefficient in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Ren Physiol. 1984;7(6):357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann K. J., Tangelder M. M., Lange W. P., Schrijver G., Koene R. A. Anti-GBM nephritis in the mouse: severe proteinuria in the heterologous phase. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;406(3):285–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00704298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann K. J., van Son J. P., Koene R. A. Improved method for the isolation of mouse glomeruli. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Oct;2(4):944–946. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V24944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Anti-DNA antibodies and lupus nephritis: the complexity of crossreactivity. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90095-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Mazzucco G., Monga G., Roffinello C., Alberton M., Dellabona P., Malavasi F., Vercellone A. Platelet cationic proteins are present in glomeruli of lupus nephritis patients. Kidney Int. 1986 Oct;30(4):555–565. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Segoloni G., Coda R., Vercellone A. Localization of neutrophil cationic proteins and loss of anionic charges in glomeruli of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Sep;24(3):299–314. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo T., Graves K., Granholm N. A. Murine lupus nephritis. Effects of glucocorticoid on glomerular permeability. Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;50(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. P., Surma M. L. Effect of diabetes on in vivo metabolism of [35S]-labeled glomerular basement membrane. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):8–12. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Rennke H. G. Anionic sites and the mechanisms of proteinuria. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 27;309(17):1050–1052. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310273091709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillit H., Lahita R. Antibodies to vascular heparan sulfate proteoglycan in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 1991;9(2):159–164. doi: 10.3109/08916939109006752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groggel G. C., Stevenson J., Hovingh P., Linker A., Border W. A. Changes in heparan sulfate correlate with increased glomerular permeability. Kidney Int. 1988 Feb;33(2):517–523. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hnatowich D. J., Virzi F., Rusckowski M. Investigations of avidin and biotin for imaging applications. J Nucl Med. 1987 Aug;28(8):1294–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Shearer T. P., Shaffer S. J. Acute reversible proteinuria induced by infusion of the polycation hexadimethrine. Kidney Int. 1981 Jul;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Linker A., Farquhar M. G. Increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to ferritin after removal of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulfate) by enzyme digestion. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):688–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Liu Z. Z., Kashihara N., Wallner E. I. Current status of the structural and functional basis of glomerular filtration and proteinuria. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Jul;11(4):390–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Rosenzweig L. J., Linker A., Jakubowski M. L. Decreased de novo synthesis of glomerular proteoglycans in diabetes: biochemical and autoradiographic evidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2272–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashihara N., Makino H., Szekanecz Z., Waltenbaugh C. R., Kanwar Y. S. Nephritogenicity of anti-proteoglycan antibodies in experimental murine lupus nephritis. Lab Invest. 1992 Dec;67(6):752–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Cavallo T. Glomerular permeability: focal loss of anionic sites in glomeruli of proteinuric mice with lupus nephritis. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Cavallo T. Glomerular permeability: transfer of native ferritin in glomeruli with decreased anionic sites. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):547–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramers C., Hylkema M. N., van Bruggen M. C., van de Lagemaat R., Dijkman H. B., Assmann K. J., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-nucleosome antibodies complexed to nucleosomal antigens show anti-DNA reactivity and bind to rat glomerular basement membrane in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):568–577. doi: 10.1172/JCI117371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramers C., Termaat R. M., ter Borg E. J., van Bruggen M. C., Kallenberg C. G., Berden J. H. Higher anti-heparan sulphate reactivity during systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease exacerbations with renal manifestations; a long term prospective analysis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jul;93(1):34–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb06493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick G. F., Ladoulis C. T., Cavallo T. Decreased anionic groups and increased permeability precedes deposition of immune complexes in the glomerular capillary wall. Am J Pathol. 1981 Nov;105(2):114–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Ben-Yehuda A., Madaio M. P., Bar-Tana R., Schuger L., Pizov G., Neeman Z. V., Cohen I. R. Binding of anti-DNA antibodies and inhibition of glomerulonephritis in MRL-lpr/lpr mice by heparin. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Oct;33(10):1554–1559. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy N., Spiro R. G. Effect of diabetes on the glycosaminoglycan component of the human glomerular basement membrane. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):738–741. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbach D. H., Wagner C. W., Star V. L., Martin G. R., Brown K. S., Yoon J. W. Reduced synthesis of basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11672–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig L. J., Kanwar Y. S. Removal of sulfated (heparan sulfate) or nonsulfated (hyaluronic acid) glycosaminoglycans results in increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to 125I-bovine serum albumin. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):177–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T., Stoeckl F., Muller S., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S., Woitas R., Vogt A. Glomerular immune deposits in murine lupus models may contain histones. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura H., Spiro R. G. Studies on macromolecular components of human glomerular basement membrane and alterations in diabetes. Decreased levels of heparan sulfate proteoglycan and laminin. Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):374–381. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenburg-Hatzopoulos C., Assel E., Schurek H. J., Stolte H. Glomerular albumin leakage and morphology after neutralization of polyanions. II. Discrepancy of protamine induced albuminuria and fine structure of the glomerular filtration barrier. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1984 Oct;16(4):741–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöckl F., Muller S., Batsford S., Schmiedeke T., Waldherr R., Andrassy K., Sugisaki Y., Nakabayashi K., Nagasawa T., Rodriguez-Iturbe B. A role for histones and ubiquitin in lupus nephritis? Clin Nephrol. 1994 Jan;41(1):10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki T., Takase S. Composition of immune deposits present in glomeruli of NZB/W F1 mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Dec;61(3):296–308. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(05)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamsma J. T., van den Born J., Bruijn J. A., Assmann K. J., Weening J. J., Berden J. H., Wieslander J., Schrama E., Hermans J., Veerkamp J. H. Expression of glomerular extracellular matrix components in human diabetic nephropathy: decrease of heparan sulphate in the glomerular basement membrane. Diabetologia. 1994 Mar;37(3):313–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00398060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Assmann K. J., Dijkman H. B., van Gompel F., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-DNA antibodies can bind to the glomerulus via two distinct mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1363–1371. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., Nossent J. C., Swaak A. J., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-heparan sulphate reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with renal or non-renal manifestations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., van Gompel F., van den Heuvel L. P., Veerkamp J. H., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate is mediated via bound DNA/histone complexes. J Autoimmun. 1990 Oct;3(5):531–545. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehaskari V. M., Root E. R., Germuth F. G., Jr, Robson A. M. Glomerular charge and urinary protein excretion: effects of systemic and intrarenal polycation infusion in the rat. Kidney Int. 1982 Aug;22(2):127–135. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Michael A. F., Velosa J., Fish A. J. Detection of hidden nephritogenic antigen determinants in human renal and nonrenal basement membranes. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):156–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Lest C. H., Versteeg E. M., Veerkamp J. H., van Kuppevelt T. H. Quantification and characterization of glycosaminoglycans at the nanogram level by a combined azure A-silver staining in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1994 Sep;221(2):356–361. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Berden J. H. A monoclonal antibody against GBM heparan sulfate induces an acute selective proteinuria in rats. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–123. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Berden J. H. Monoclonal antibodies against the protein core and glycosaminoglycan side chain of glomerular basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan: characterization and immunohistological application in human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Jan;42(1):89–102. doi: 10.1177/42.1.8263327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Weening J. J., Berden J. H. Distribution of GBM heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein and side chains in human glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 1993 Feb;43(2):454–463. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel L. P., van den Born J., van de Velden T. J., Veerkamp J. H., Monnens L. A., Schroder C. H., Berden J. H. Isolation and partial characterization of heparan sulphate proteoglycan from the human glomerular basement membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):457–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2640457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]