Abstract
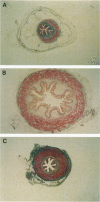
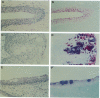
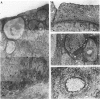
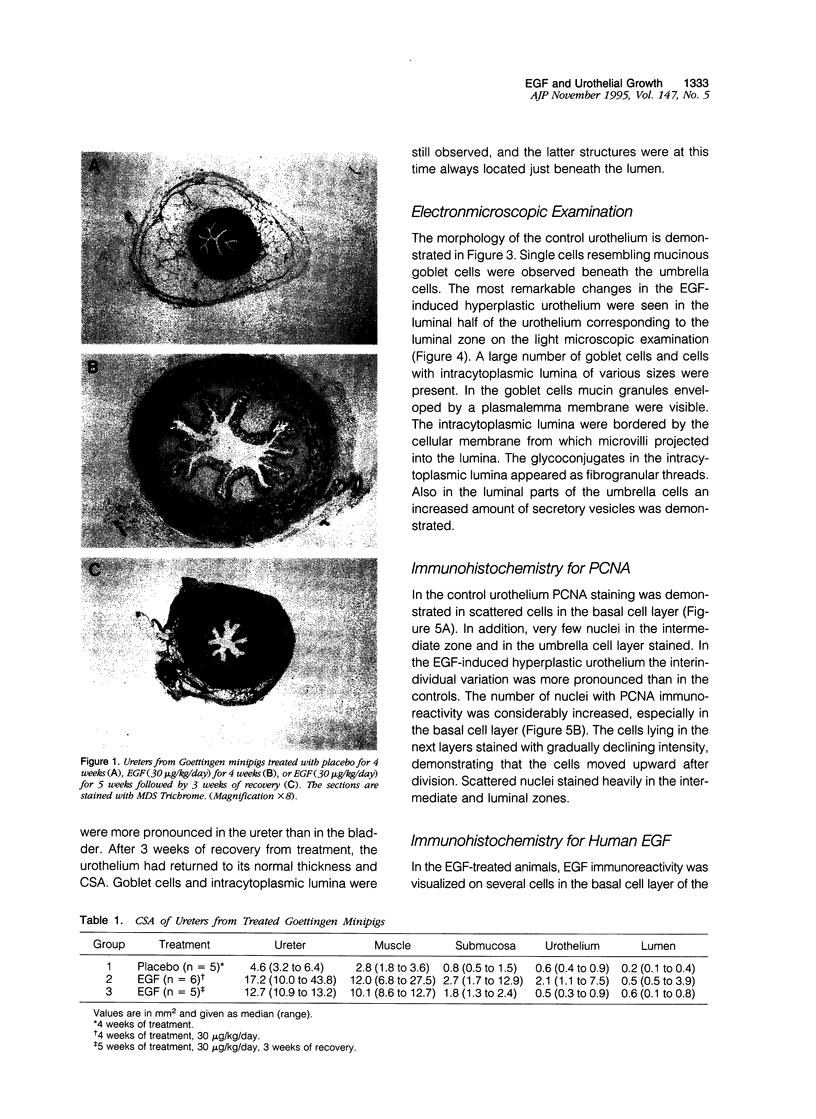
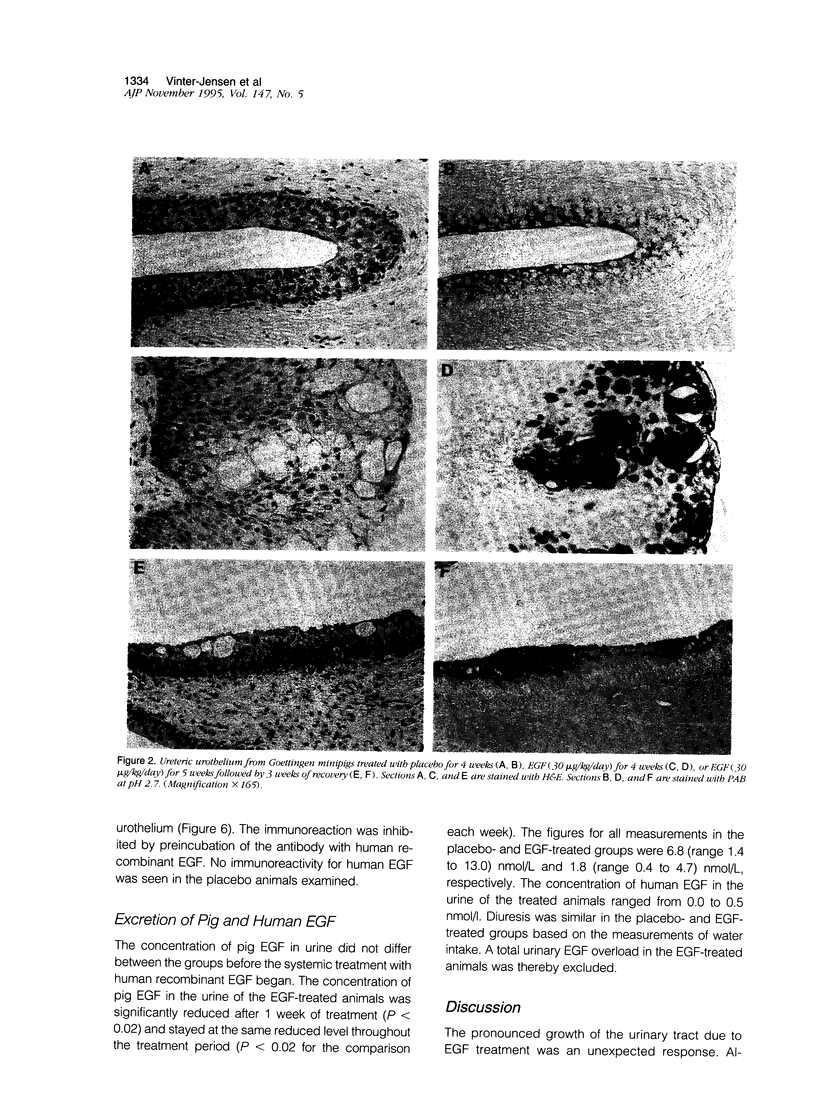
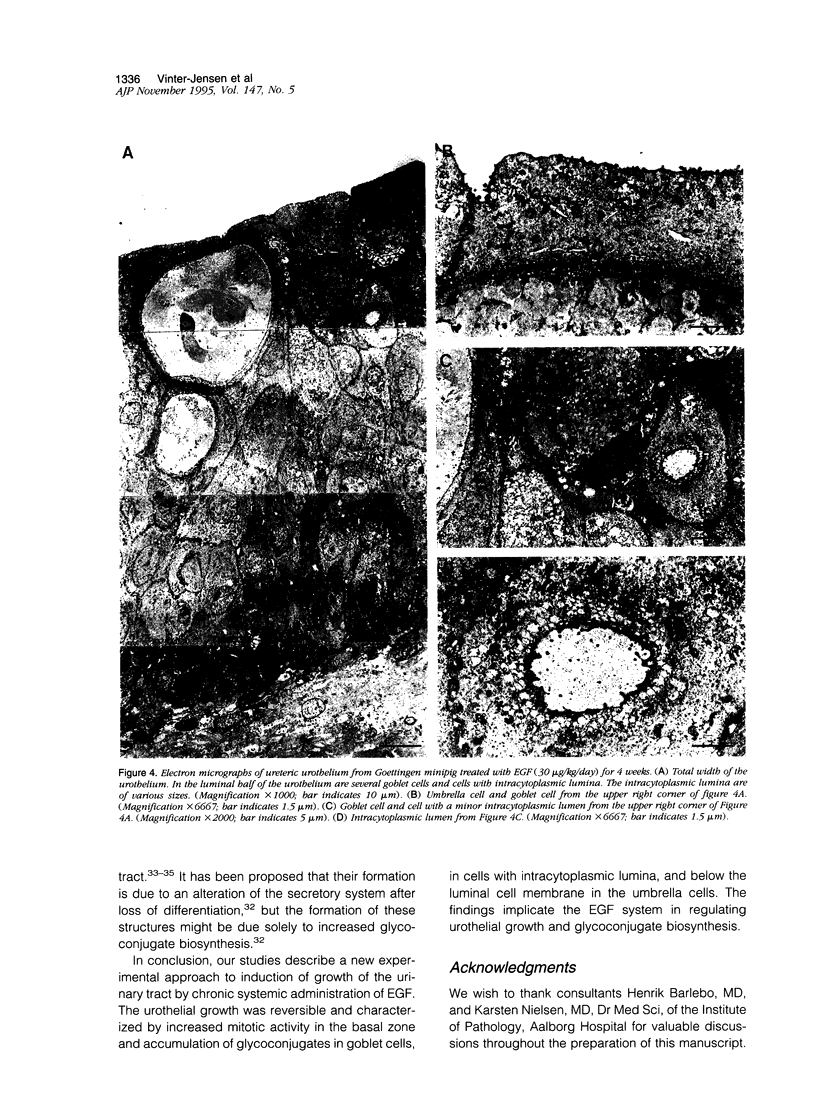
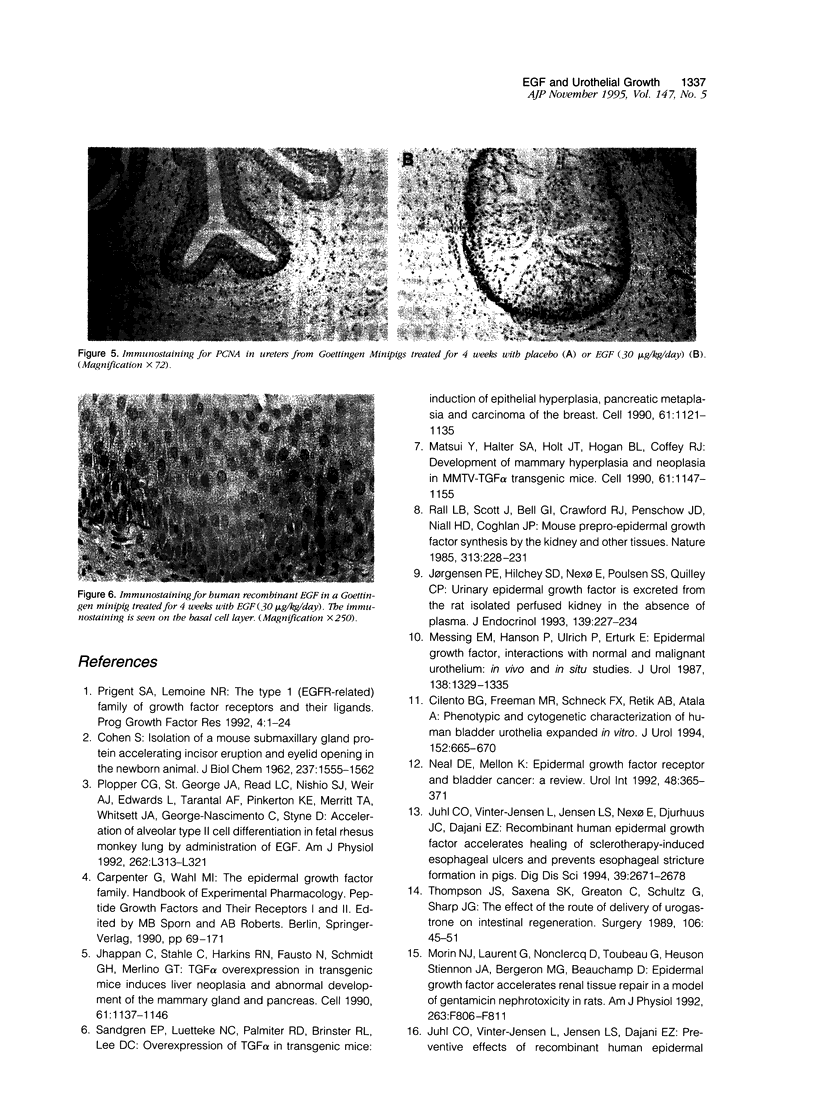
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is present in large amounts in the urine, but the effects of systemically administered EGF on the urinary tract have not been described previously. In the present paper, we describe a potent growth induction of EGF on the urinary tract. Goettingen minipigs were treated with solvent (n = 5), EGF 30 micrograms/kg/day (n = 6) for 4 weeks, or EGF 30 micrograms/kg/day for 5 weeks followed by 3 weeks of recovery (n = 5). The ureters and bladders were examined by routine histology and electron microscopy and were immunostained for proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Four weeks of EGF treatment increased the median cross sectional area of the ureter fourfold with growth of all wall layers. The urothelium was widened from 5 cell layers in the controls to 10 in the EGF-treated animals. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunostaining revealed an increased mitotic activity in the basal zone of the urothelium. In the luminal zone, glycoconjugates accumulated in goblet cells, in cells with intracytoplasmic lumina, and beneath the luminal cell membrane in the umbrella cells. Our studies present a new experimental approach to growth induction of the urinary tract. The findings implicate the EGF system in regulating urothelial growth and glycoconjugate biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alroy J., Pauli B. U., Hayden J. E., Gould V. E. Intracytoplasmic lumina in bladder carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 1979 Sep;10(5):549–555. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(79)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R. Growth regulation of the PCNA gene. J Cell Sci. 1991 Apr;98(Pt 4):433–436. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cilento B. G., Freeman M. R., Schneck F. X., Retik A. B., Atala A. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characterization of human bladder urothelia expanded in vitro. J Urol. 1994 Aug;152(2 Pt 2):665–670. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)32676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill W. B., Ruggiero K., Straus F. H., 2nd Crystallization studies in a urothelial-lined living test tube (the catheterized female rat bladder). I. Calcium oxalate crystal adhesion to the chemically injured rat bladder. Invest Urol. 1979 Nov;17(3):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guglietta A., Lesch C. A., Romano M., McClure R. W., Coffey R. J. Effect of transforming growth factor-alpha on gastric acid secretion in rats and monkeys. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Jan;39(1):177–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02090079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Coates P. J., Goodlad R. A., Hart I. R., lane D. P. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in non-cycling cells may be induced by growth factors in vivo. Br J Cancer. 1994 Aug;70(2):244–247. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen L. S., Krarup N., Larsen J. A., Juhl C., Nielsen T. H., Dybdahl H. Chronic portal venous hypertension. The effect on liver blood flow and liver function and the development of esophageal varices. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 May;22(4):463–470. doi: 10.3109/00365528708991492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhl C. O., Vinter-Jensen L., Jensen L. S., Nexø E., Djurhuus J. C., Dajani E. Z. Systemic treatment with recombinant human epidermal growth factor accelerates healing of sclerotherapy-induced esophageal ulcers and prevents esophageal stricture formations in pigs. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Dec;39(12):2671–2678. doi: 10.1007/BF02087708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. E., Hilchey S. D., Nexø E., Poulsen S. S., Quilley C. P. Urinary epidermal growth factor is excreted from the rat isolated perfused kidney in the absence of plasma. J Endocrinol. 1993 Nov;139(2):227–234. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1390227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. E., Rasmussen T. N., Skov Olsen P., Raaberg L., Seier Poulsen S., Nexø E. Renal uptake and excretion of epidermal growth factor from plasma in the rat. Regul Pept. 1990 May 21;28(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90025-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Halter S. A., Holt J. T., Hogan B. L., Coffey R. J. Development of mammary hyperplasia and neoplasia in MMTV-TGF alpha transgenic mice. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1147–1155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90077-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing E. M., Hanson P., Ulrich P., Erturk E. Epidermal growth factor--interactions with normal and malignant urothelium: in vivo and in situ studies. J Urol. 1987 Nov;138(5):1329–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin N. J., Laurent G., Nonclercq D., Toubeau G., Heuson-Stiennon J. A., Bergeron M. G., Beauchamp D. Epidermal growth factor accelerates renal tissue repair in a model of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F806–F811. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal D. E., Mellon K. Epidermal growth factor receptor and bladder cancer: a review. Urol Int. 1992;48(4):365–371. doi: 10.1159/000282357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø E., Jørgensen E., Hansen M. R. Human epidermal growth factor-on molecular forms present in urine and blood. Regul Pept. 1992 Nov 20;42(1-2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(92)90025-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen P. S., Poulsen S. S., Kirkegaard P., Nexø E. Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. L., Mulholland S. G. Bladder surface mucin. Its antibacterial effect against various bacterial species. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):423–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plopper C. G., St George J. A., Read L. C., Nishio S. J., Weir A. J., Edwards L., Tarantal A. F., Pinkerton K. E., Merritt T. A., Whitsett J. A. Acceleration of alveolar type II cell differentiation in fetal rhesus monkey lung by administration of EGF. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L313–L321. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent S. A., Lemoine N. R. The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1992;4(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(92)90002-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quincey C., Raitt N., Bell J., Ellis I. O. Intracytoplasmic lumina--a useful diagnostic feature of adenocarcinomas. Histopathology. 1991 Jul;19(1):83–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Crawford R. J., Penschow J. D., Niall H. D., Coghlan J. P. Mouse prepro-epidermal growth factor synthesis by the kidney and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):228–231. doi: 10.1038/313228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy L. The intracellular lumen: origin, role and implications of a cytoplasmic neostructure. Biol Cell. 1986;56(2):97–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1986.tb00446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Luetteke N. C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lee D. C. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1121–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90075-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrinho-Simões M., Johannessen J. V., Gould V. E. The diagnostic significance of intracytoplasmic lumina in metastatic neoplasms. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1981 Oct-Dec;2(4):327–335. doi: 10.3109/01913128109081980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate J., Hutton K. A., Thomas D. F., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Normal human urothelial cells in vitro: proliferation and induction of stratification. Lab Invest. 1994 Oct;71(4):583–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Yang S., Schwartz M. S. Epidermal growth factor-like growth factors. I. Breast malignancies and other epithelial proliferations in transgenic mice. Lab Invest. 1993 Dec;69(6):660–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Saxena S. K., Greaton C., Schultz G., Sharp J. G. The effect of the route of delivery of urogastrone on intestinal regeneration. Surgery. 1989 Jul;106(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan T. J., Pascall J. C., James P. S., Brown K. D. Expression of epidermal growth factor and its mRNA in pig kidney, pancreas and other tissues. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):315–318. doi: 10.1042/bj2790315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinter-Jensen L., Frøkiaer J., Jørgensen P. E., Marqversen J., Rehling M., Dajani E. Z., Nexø E. Tissue distribution of 131I-labelled epidermal growth factor in the pig visualized by dynamic scintigraphy. J Endocrinol. 1995 Jan;144(1):5–12. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1440005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]