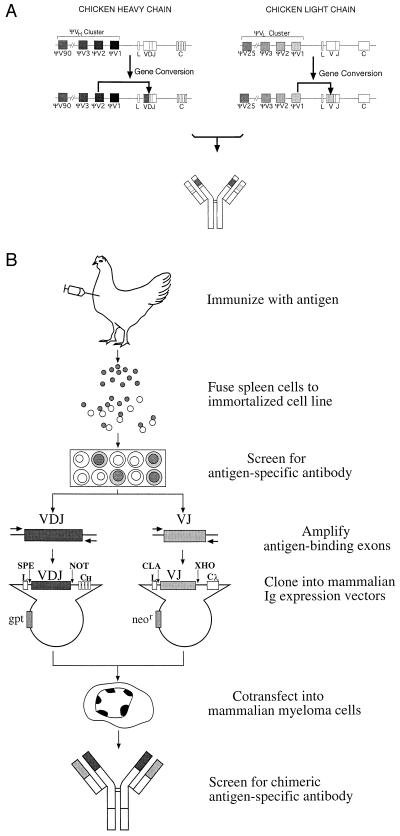
Figure 1.
Chickens create antibody diversity by a mechanism that can be exploited to generate a new type of mAb. (A) Diagram of the chicken Ig loci illustrating the process of Ig diversification by intrachromosomal gene conversion. The genomic loci of the chicken IgH and IgL chains contain only single functional V and J gene segments. Therefore, V(D)J recombination does not result in combinational diversity. Instead, Ig diversity occurs by the sequential unidirectional transfer of sequences from the upstream pseudo-V (ΨV) gene segments to the expressed V region by intrachromosomal gene conversion; a single gene conversion event at each locus is diagrammed on the second line. The antibody produced by the assembly of diversified heavy and light chains is indicated below. (B) The flow chart depicts the major steps in the process of producing chicken-derived mAbs, described in detail in the text.