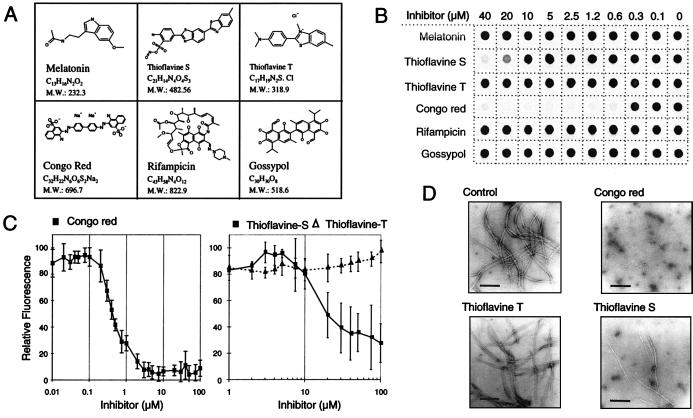
Figure 2.
Inhibition of HD exon 1 aggregation by small molecules. (A) Structure of the chemical compounds examined for their ability to inhibit HD exon 1 fibrillogenesis. (B) Effect of various concentrations of the indicated chemical compounds on HD exon 1 aggregation as monitored by the filter retardation assay. GST-HD51 fusion protein at a conc. of 2.5 μM was predigested for 30 min at 37°C with trypsin at an enzyme/substrate ratio of 1:10 (wt/wt). Then chemical compounds were added to the cleavage reactions to give the indicated final concentration. Reaction mixtures were incubated for an additional 18 h at 37°C and insoluble polyQ-containing HD51 aggregates were detected by the filter retardation assay. (C) Quantification of the dot blot results obtained with Congo red, thioflavine S, and thioflavine T. The signal intensity obtained from the sample without added chemical compound was arbitrarily set as 100. Values shown are the average of triplicate incubations ± SE. (D) Electron micrographs of HD51 fibrils formed in the presence or absence of the indicated chemical compounds. Trypsin-digested GST-HD51 protein at 2.5 μM was incubated at 37°C for 24 h either without added chemical compound (control) or with Congo red (final conc. 2.5 μM), thioflavine T, and thioflavine S (final conc. 40 μM each). Representative samples of fibrillar structures are shown. (Bar = 200 nm.)