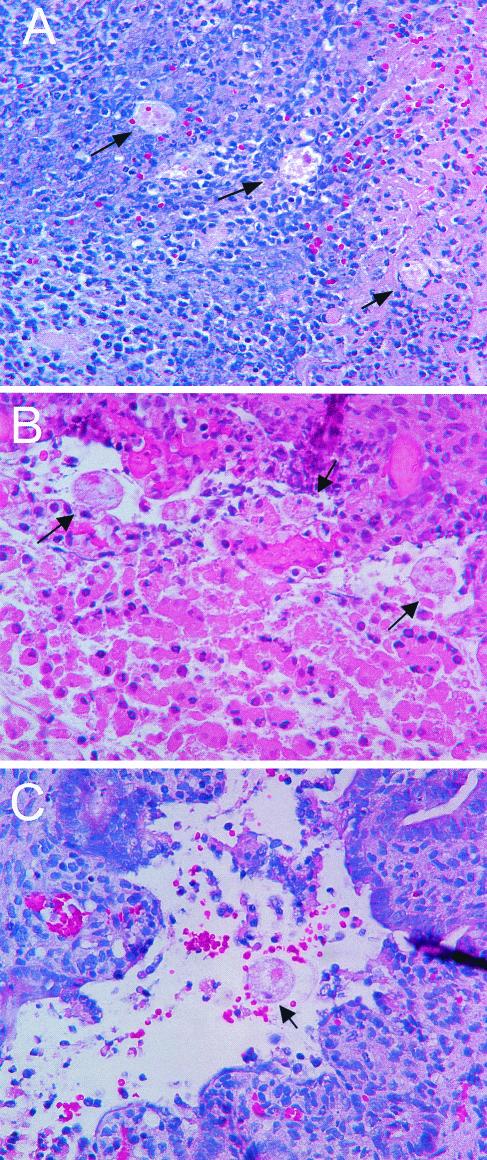
FIG. 2.
Morphological findings on E. histolytica-infected human colonic xenografts from SCID-HU-INT mice. Photomicrographs of hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained sections of E. histolytica-infected human colonic xenografts from an untreated SCID-HU-INT mouse (A), an anti-TNF-α-treated SCID-HU-INT mouse (B), and an IL-1ra-treated mouse (C) are shown. Extensive mucosal destruction and inflammation with neutrophil infiltration and multiple E. histolytica trophozoites (arrows) that have invaded the mucosa and submucosal tissues are visible in the section from the untreated SCID-HU-INT mouse (A). In the E. histolytica-infected human colonic xenograft from the anti-TNF-α-treated mouse, extensive mucosal damage and multiple invading E. histolytica trophozoites are also visible (arrows) but no marked cellular infiltrate is present (B). In the E. histolytica-infected human colonic xenograft from the IL-1ra-treated mouse (C), extensive mucosal damage and hemorrhage are present near a single E. histolytica trophozoite (arrow) but no marked neutrophilic infiltration is apparent. Original magnification of all three panels, ×400.