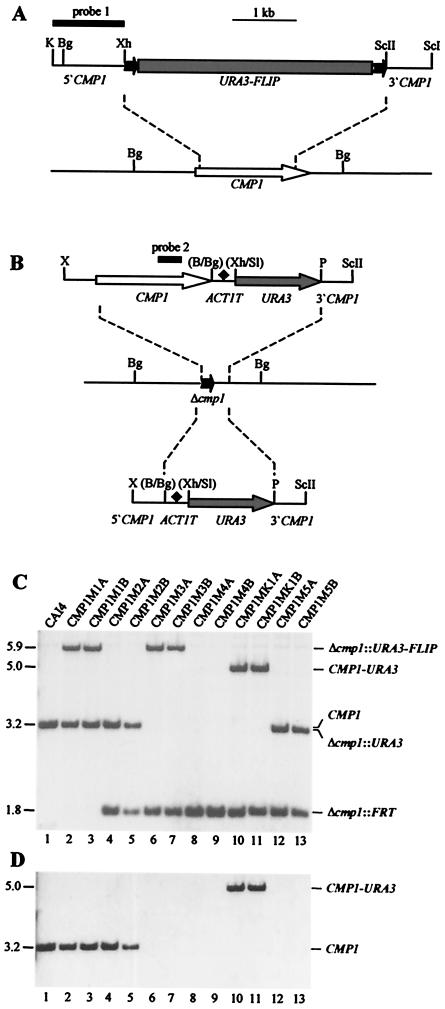
FIG. 2.
Construction of C. albicans cmp1 deletion mutants and complemented strains. (A) Structure of the deletion cassette from plasmid pCMP1M2 (top) and genomic structure of the CMP1 locus in the parent strain, CAI4 (bottom). The CMP1 coding region is represented by the open arrow, and the upstream and downstream sequences are represented by solid lines. Details of the URA3 flipper (shaded rectangle bordered by FRT sites [solid arrows]) have been presented elsewhere (39). The 34-bp FRT sites are not drawn to scale. The DNA fragment used for Southern hybridization analysis of the mutants is represented by the thick bar (probe 1). (B) Structures of the DNA fragments from pCMP1K1 (top) and pCMP1M4 (bottom), which were used for reintegration of an intact CMP1 copy (open arrow) or only the URA3 marker (shaded arrows), respectively, into one of the inactivated cmp1 alleles (middle). The ACT1 transcription termination sequence (ACT1T) is indicated by the solid diamond. Only relevant restriction sites are given. B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; K, KpnI; P, PstI; ScI, SacI; ScII, SacII; Sl, SalI; X, XbaI; Xh, XhoI. The restriction sites shown in parentheses were destroyed by the cloning procedure. The CMP1 internal fragment used for Southern hybridization analysis of the strains is indicated by the thick bar (probe 2). (C) Southern hybridization of BglII-digested genomic DNAs of the parent strain, CAI4, and mutant derivatives with the CMP1 probe 1. The sizes of the hybridizing fragments (in kilobases) are given on the left side of the blot, and their identities are indicated on the right. (D) Rehybridization of the same blot with a CMP1 internal fragment (probe 2).