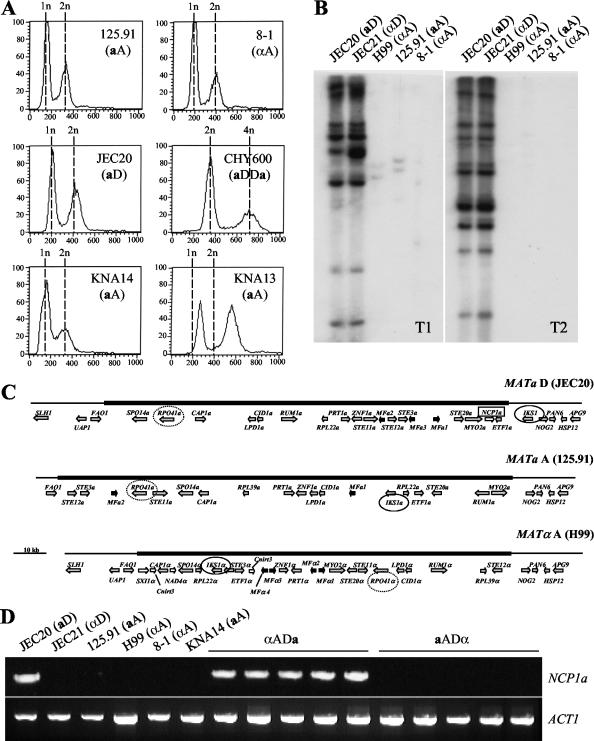
FIG. 1.
Identification of a and α haploid serotype A C. neoformans strains. (A) FACS analysis of the aA strains 125.91, KNA13, and KNA14; the αA strain 8-1; and the control aD haploid strain JEC20 and aDDa diploid strain CHY600. (B) Southern blots of 125.91 (aA), 8-1 (αA), H99 (αA), JEC20 (aD), and JEC21 (αD) PstI-digested genomic DNAs probed with transposon T1 or transposon T2. (C) Structures of the MAT locus alleles from the aD strain JEC20, the aA strain 125.91, and the αA strain H99. The mating type-specific regions are shown as thick lines, and the flanking regions are shown as thin lines. Genes are represented as arrows in the direction of transcription. Genes encoding pheromones are shown as black arrows, locus-specific genes are shown as white arrows, and all other genes are in grey. The IKS1 genes are circled with a black line, the RPO41 genes are circled with a dotted line, and the NCP1a gene is boxed. (D) PCR assays were conducted with primers specific to NCP1a. Genomic DNAs from serotype D, serotype A, and AD hybrid strains were assayed. aADα hybrid strains were ZG290, ATCC 48184, CDC92-74 (ADα), CDC228, and CDC304. αADa hybrid strains were ZG287, MMRL774, KW5, CBS132, and CDC94-383. PCR with primers specific to the actin gene served as a positive control for the presence of genomic DNA.