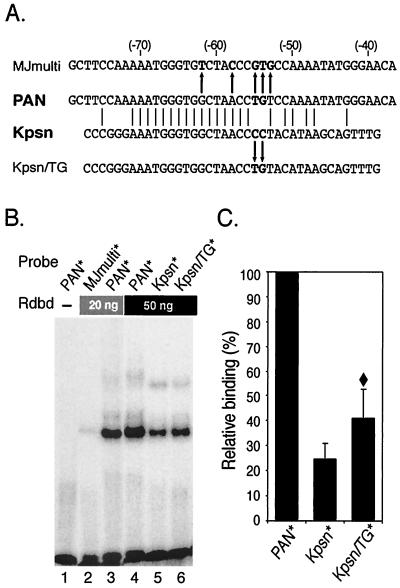
FIG. 1.
RTA DNA-binding domain protein (Rdbd) binds a Kpsn promoter sequence which is highly homologous to the RRE of the PAN promoter. (A) Comparison of the pPAN RRE and the homologous Kpsn promoter sequence. The pPAN RRE (PAN) shares significant homology to the Kpsn promoter sequence, and matched sequences are aligned. MJmulti is a mutant version of pPAN RRE with 5 nt mismatched (44), as indicated with arrows. For Kpsn/TG, a mutation of Kpsn (CC→TG) was introduced to further liken Kpsn to pPAN RRE. (B) EMSA of PAN*, MJmulti*, Kpsn*, and Kpsn/TG*. End-labeled probes were incubated with 0, 20, or 50 ng of Rdbd, as indicated. Rdbd was expressed in bacteria with a FLAG peptide at the N terminus and 6× histidine residues at the C terminus and purified using a Ni+-nitrilotriacetic acid column. (C) Quantitative analysis of Rdbd binding. Rdbd binding affinities to Kpsn* and Kpsn/TG* were calculated relative to those for PAN*. The values represent averages of relative binding affinities from three independent EMSAs, with the standard deviation shown. A diamond symbol (♦) indicates statistically significant difference in Rdbd binding between Kpsn* and Kpsn/TG* (P < 0.05, t test).