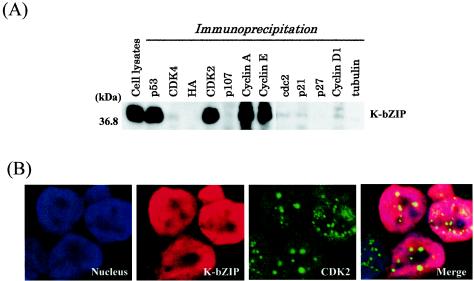
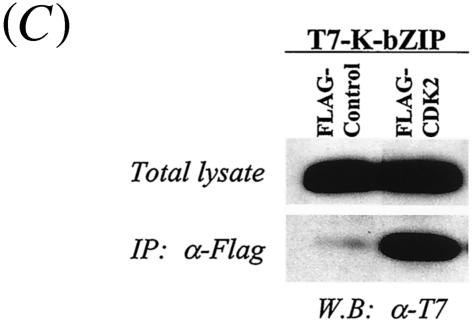
FIG. 2.
Coimmunoprecipitation assay. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation assay with the KSHV-positive BCBL-1 cell line. BCBL-1 cells induced to viral lytic replication with TPA (48 h) were harvested with EBC buffer, and the same amounts of lysates (500 μg) were precipitated with antibodies against different molecules and then immunoblotted with anti-K-bZIP rabbit serum. (B) Colocalization of K-bZIP with CDK2. Confocal analysis was performed with anti-K-bZIP rabbit serum and anti-CDK2 mouse monoclonal antibody 48 h after TPA induction. K-bZIP (red) and CDK2 (green) were detected with Alexa Fluor 555-conjugated goat F(ab′)2 anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat F(ab′)2 anti-mouse immunoglobulin G. The nucleus was counterstained with To-Pro-3 (blue). This panel is representative of 10 different fields. (C) Association between K-bZIP and CDK2-cyclins in 293T cells. 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. Cell lysates were precipitated with Flag antibody-conjugated agarose, and coimmunoprecipitation of K-bZIP was detected with anti-T7 antibody. The expression of T7-tagged K-bZIP in total lysates is shown in the same blots as a control. IP, immunoprecipitation; W.B, Western blotting; α, anti.