FIG. 1.
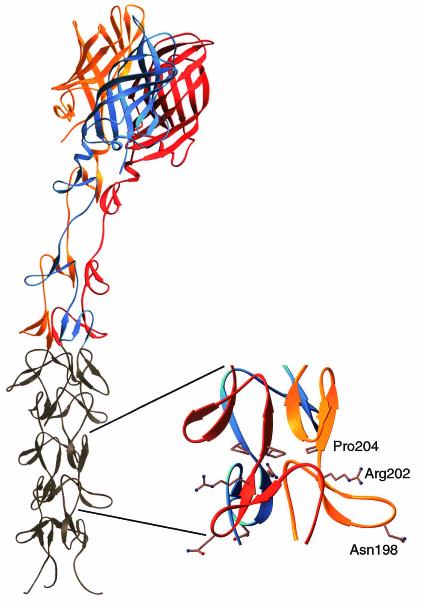
Crystal structure of reovirus attachment protein σ1. The crystal structure of T3D σ1 includes residues 245 to 455 (14). The three monomers of the σ1 trimer are shown in red, orange, and blue. Each monomer consists of a C-terminal head domain formed by a compact β-barrel and an N-terminal fibrous tail that contains three β-spiral repeats. Based on analysis of patterns in aligned σ1 sequences, the β-spiral likely begins at residue 167 of T3D σ1 and comprises eight repeats. The N-terminal five repeats, which are not included in the crystal structure, are shown in gray. The spiral has been extended using translated and rotated σ1 repeats to generate a model that depicts the approximate dimensions of the molecule. Amino acids Asn198, Arg202, and Pro204 have been implicated in the interaction of T3D σ1 with sialic acid (13). The approximate location of these residues in the model (shown in ball-and-stick representation on the right) suggests that they form a binding site for sialic acid. Residues 1 to 167 are not shown; these residues are predicted to form a triple α-helical coiled coil structure (6, 25, 27, 40). This figure was prepared by Thilo Stehle (Harvard University) (published with permission) with the program RIBBONS (10).