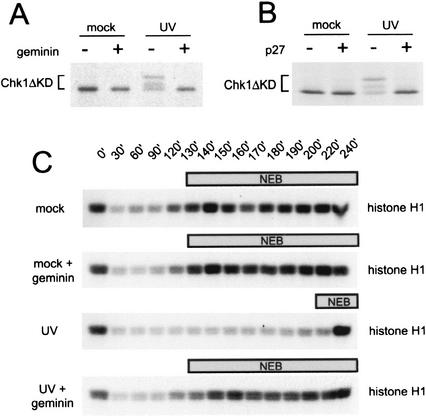
Figure 3.
Loss of the DNA damage checkpoint response after inhibition of DNA replication. (A) Phosphorylation of xChk1 (Chk1ΔKD) in Xenopus interphase extract after geminin treatment. Mock-treated or UV-damaged sperm chromatin (2000/μL) was added to mock- or geminin-pretreated extract containing Chk1ΔKD, and samples were analyzed as described in Figure 1A. (B) Phosphorylation of xChk1 (Chk1ΔKD) in Xenopus interphase extract after p27 treatment. Mock-treated or UV-damaged sperm chromatin (2000/μL) was added to mock- or p27-pretreated extract containing Chk1ΔKD, and samples were analyzed as described in Figure 1A. (C) Phosphorylation of histone H1 in mock- or geminin-treated cytostatic-factor-arrested (CSF) extract. CSF extract pretreated with buffer or recombinant geminin was supplemented with mock- or UV-treated sperm nuclei and 1 mM CaCl2. At the indicated time points, samples were removed to assay histone H1 kinase activity. The time at which nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB) was >50% is indicated by the bar above each panel.