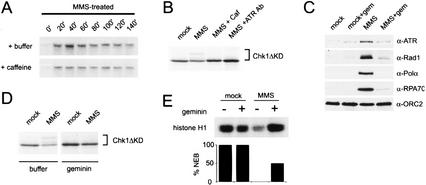
Figure 4.
Activation of the MMS checkpoint is replication-dependent. (A) DNA replication is slowed after MMS damage. Chromatin was pretreated with MMS, and replication was assayed as described in Figure 1A. See Figure 1A for untreated control (+/−) caffeine. (B) Phosphorylation of xChk1ΔKD induced by MMS was assayed after treatment of the extract with the checkpoint kinase inhibitor caffeine (4 mM) or an xATR-neutralizing antibody (10% reaction volume) as described in Figure 1A. (C) Chromatin was isolated from mock- or geminin-treated extract containing mock- or MMS-treated chromatin after 100 min, and chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed as described in Figure 2. (D) MMS-induced phosphorylation of xChk1ΔKD was assayed after geminin treatment. Geminin-treated interphase extract was supplemented with xChk1ΔKD and sperm chromatin (3000/μL), and samples were harvested at 100 min. Sperm nuclei were treated with MMS prior to addition to the extract. (E) Histone H1 kinase activity and percentage of nuclear envelope breakdown (%NEB) were assayed in CSF extract at 160 min. Extract was pretreated with buffer or geminin, and sperm chromatin was mock-treated or treated with MMS prior to addition to extract.