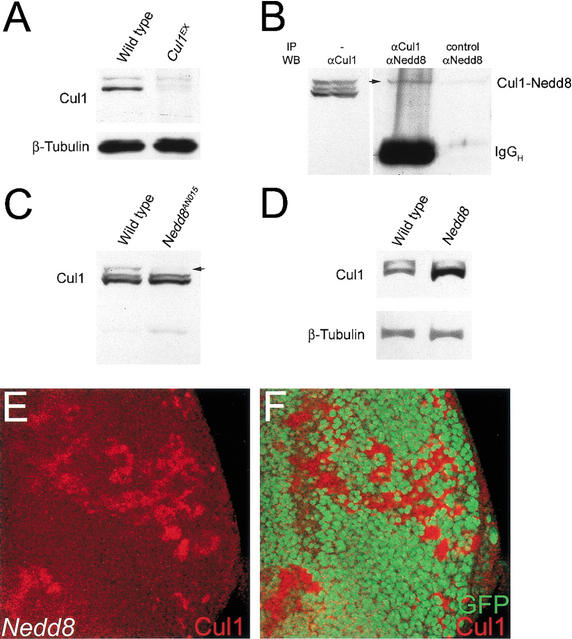
Figure 4.
Nedd8 modifies Cul1 and controls its stability. (A) Western blot by αCul1 antibodies. Cell extracts were prepared from first-instar larvae of wild-type (left lane) and Cul1EX mutant (right lane). The levels of Cul1 proteins of 90 kD are greatly reduced in Cul1EX cell extract. (B) Conjugation of Nedd8 to Cul1. Western blot of cell extract prepared from the eye discs and brain lobes of third-instar larvae by αCul1 antibodies (left lane). Immunocomplex of Cul1 from precipitation by αCul1 antibodies is blotted by αNedd8 antibodies (middle lane). An arrow indicates the putative Nedd8-modified Cul1 form. In the control experiment without the addition of αCul1 antibodies in precipitation, no Nedd8 positive signal can be detected (right lane). (C) Immunoblotting of cell extract prepared from first-instar larvae of wild-type (left lane) and Nedd8AN015 (right lane) by αCul1 antibodies. The Nedd8-modified form of Cul1 is missing in Nedd8 larvae (right lane, arrow). (D) In the absence of Nedd8 modification, the Cul1 level is increased. Western blot analysis of cell extract from third-instar eye discs and brain lobes by αCul1 antibodies indicates that the Cul1 protein is accumulated in Nedd8AN015/Nedd8EP(2)2063 (right lane). (E,F) A late third-instar eye disc containing Nedd8 mutant clones and stained with αCul1 antibodies (red). Cul1 accumulates in the Nedd8 mutant clones (red in E) that are marked by the lack of GFP expression (green in F).