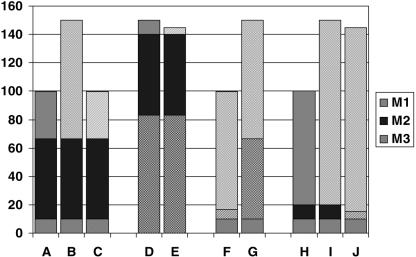
Figure 1.
a: normal physiology: 3 molecular mechanisms (M1, M2, M3) contribute to a trait; b: diseased physiology D1: derailment (cause/contribution) of molecular mechanism 1 (M1); c: diseased physiology D1: causal treatment T1 (aimed at M1); d: diseased physiology D3: derailment (cause/contribution) of molecular mechanism 3 (M3); e: diseased physiology D3, treatment T1: treatment does not address cause; f: diseased physiology D1, palliative treatment T2 (aimed at M2); g: diseased physiology D1, palliative treatment T2; T2-refractroy gene variant in M2; h: normal physiology variant: differential contribution of M1 and M2 to normal trait; i: diseased physiology D1-variant: derailment of mechanism M1; j: diseased physiology D1-variant: treatment with T2.