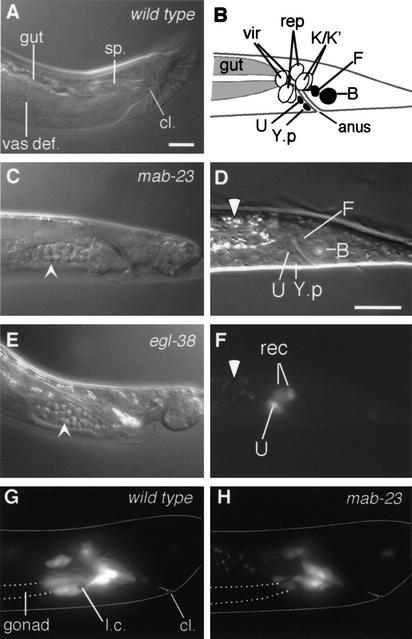
Figure 6.
mab-23 is required for development of the male proctodeum. (A,C,E) Proctodeum of wild-type, mab-23 and egl-38 adult males. Nomarski micrographs (lateral view; anterior, left; dorsal, up). (A) In wild-type males the vas deferens (vas def.) is devoid of sperm. cl., cloaca (the anus in larval animals); sp., spicules. In mab-23 (C) and egl-38 (E) males, sperm (arrowhead) accumulates in the vas def. (B) Schematic of L1 male hindgut (lateral view). Black, blast cells; vir, rectal valve cells; rep, rectal epithelial cells (Sulston et al. 1980). (D) Nomarski micrograph of L1 male hindgut (lateral view; anterior, left; dorsal, up). (F) Fluorescent micrograph of D showing MAB-23 ∷ GFP in U and two rectal epithelial cells (rec), either K, K.a, K‘, or repD; gut autofluorescence (white arrowhead). (G,H) Fluorescent micrograph showing plin-48 ∷ gfp-expressing hindgut cells in late L4 males (lateral view). U descendents and K‘/K.a are located over the posterior end of the gonad (outlined with broken line) in the ventral half of the animal. In wild-type (G), these cells extend anteriorly over the gonad; in mab-23 males (H), these cells show only limited extension. Body outline (solid line), engulfed linker cell corpse inside U.l/rp (l.c). Magnification, 1000×. Bar, 10 μM.