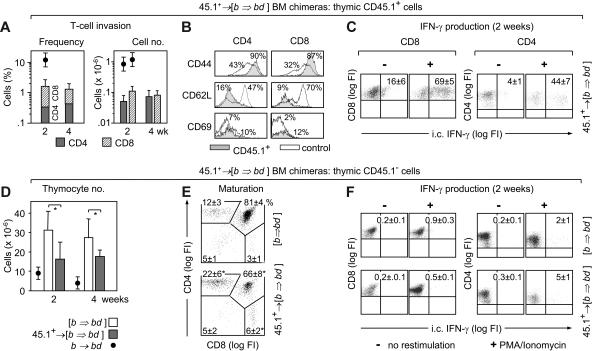
Figure 5.
Thymic donor T-cell invasion and abnormal T-cell development following inactivation of host-type pAPC. [B6→BDF1] BM chimeras (Figures S2–S3) remained untreated [b⇒bd], or received B6.CD45.1 T-cells, denoted 45.1+→ [b⇒bd]. Analysis of intrathymic CD45.1+ donor T cells (A-C) and CD45.1− host-type thymocytes (D-F). (A) Frequencies and total numbers of donor CD4+ (▩) and CD8+ (▨) T cells at 2 to 4 weeks after T-cell infusion. For comparison, donor T-cell infiltration during aGVHD in nonchimeric mice is given (●). (B) Activation markers of thymic CD45.1+ T cells (shaded) were compared to splenic T cells from naive B6 mice (not filled). The x-axes show log FI of flow cytometric analyses. Numbers depict relative frequencies (%) of cells expressing the indicated surface marker. (C) Intracytoplasmic (i.c.) IFN-γ expression by donor-derived intrathymic T cells was detected in 8 mice per group. (D) Absolute number of host-type thymocytes in 45.1+→ [b⇒bd] (▩) was compared to [b⇒bd] mice (□). (E) Frequencies of CD45.1− thymocyte populations. (F) Intracytoplasmic IFN-γ in CD45.1− thymocytes in the same mice shown in panel C. For panels A, D, and E, a total of 16 (controls) and 26 (aGVHD) mice were analyzed. Data were compiled from results of 6 experiments, with 2 to 4 animals per group. For panels B, C, and F, 8 mice (GVHD) and 4 mice (controls), respectively, were studied per group. *P < .05 versus controls.