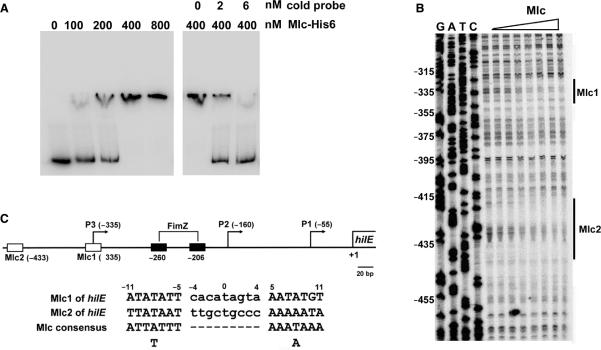
Figure 5.
The Mlc protein binds to the hilE promoter. (A) Gel mobility shift assay of hilE promoter DNA with the purified Mlc-His6 protein. Labeled hilE promoter DNA (2 nM) was incubated with 100 ng of poly dI-dC DNA competitor and various amounts of Mlc-His6, as indicated at the top of the left panel. Labeled DNA (2 nM) was mixed with 400 nM of Mlc-His6 and various concentrations of unlabeled hilE promoter DNA (cold probe), as indicated at the top of the right panel. The DNA–protein complexes were resolved by electrophoresis in a 6% polyacrylamide gel. (B) DNase I footprinting analysis of the hilE promoter DNA was performed with a probe for the non-coding strand. The hilE promoter DNA was incubated with purified Mlc-His6, which was diluted through a 2-fold series of dilutions in 1× binding buffer to the desired concentration (lanes 1–8: 0, 18.75, 37.5, 75, 150, 300, 600 and 1200 nM, respectively). The protected regions of the two Mlc sites are indicated with solid vertical lines and marked as Mlc1 and Mlc2. The numbering on the left is based on the translational start site for hilE. (C) Schematic representation of the locations of the promoters and putative protein-binding sites in the hilE promoter. The numbering is relative to the translational start site for hilE. The transcriptional start sites of P1 (−55), P2 (−160) and P3 (−335) are shown with arrows. The binding sites for Mlc and FimZ are shown by open and black boxes, respectively, and the numbers under the boxes indicate the centers of the binding sites. The sequence of each Mlc-binding site in the hilE promoter region is numbered relative to the center of the binding site and is indicated along with the consensus sequence for the Mlc-binding site. The locations of the P1 and P2 promoters and FimZ-binding sites have been reported by Baxter and Jones (18). The map is drawn to scale.