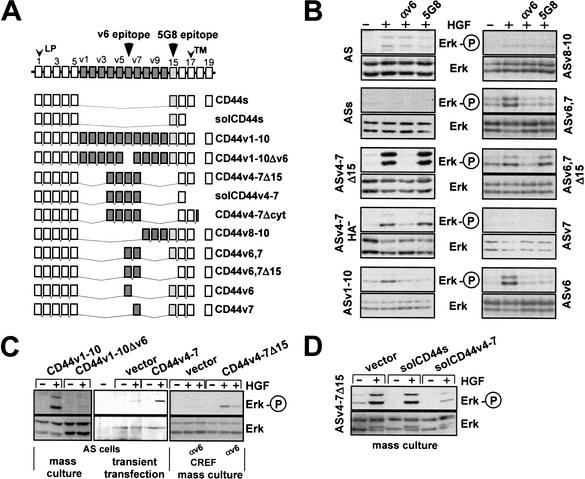
Figure 3.
CD44 isoforms containing the exon v6 sequence are required for Met activation. (A) Schematic representation of CD44 isoform structures. Constant region exons are numbered 1–5 and 15–19, variant exons v1–v10. LP, leader peptide; TM, transmembrane region. (B) Activation of Met in AS cells stably transfected with various CD44 isoforms was measured using phosphorylation of Erk as readout. The loading controls were performed by stripping the phospho-Erk blot and reprobing with an anti-Erk antibody. ASs indicates transfectants with CD44s, ASv4–7Δ15 cells stands for transfectants with CD44v4–7 with an exon 15 deletion, and ASv4–7HA− indicates cells transfected with a CD44 isoform containing a point mutation in the major hyaluronate (HA) binding site (Sleeman et al. 1997). Other transfectants are designated according to the CD44 variants used for transfection. (C) CREF or AS cells were stably transfected with CD44 constructs (Günthert et al. 1991 and as indicated) together with a plasmid harboring the puromycin resistance gene, and were grown as mass cultures. AS cells were transiently transfected with CD44v4–v7 (or vector) together with a hemagglutinin-tagged Erk (see Materials and Methods). Determination of Erk activation in response to HGF treatment is described in Materials and Methods. (D) ASv4–7Δ15 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs, and puromycin resistant clones were selected as mass cultures.