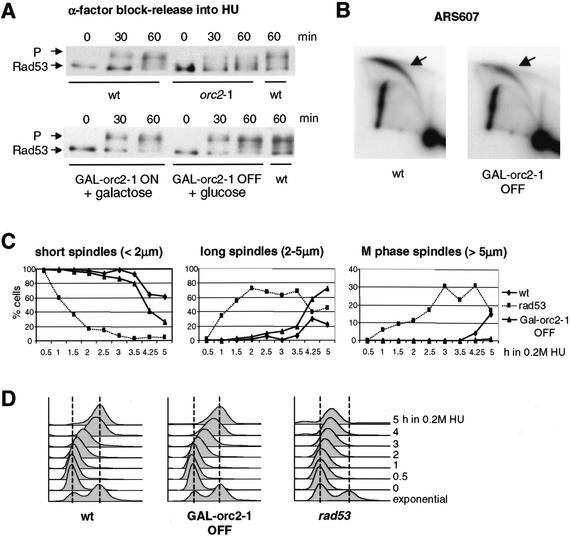
Figure 6.
The S-phase checkpoint requires ORC2 function in G1, but not in S phase. (A) Congenic wild-type (GA-1682), GAL1UAS∷orc2-1 (GA-1681), and orc2-1 (GA-1836) strains were cultured in YPA-2% galactose (YPAG) at 23°C. After synchronization in α-factor, wild-type, orc2-1, and half of the GAL1UAS∷orc2-1 (GAL∷orc2-1 OFF) cells were switched to YPAD + α-factor, whereas the other half of the GAL1UAS∷orc2-1 culture was kept on YPAG + α-factor (GAL∷orc2-1 ON). After 60 min at 30°C, cultures were washed and released from pheromone into 0.2 M HU in YPAD or YPAG at 30°C. Rad53p phosphorylation was monitored at 0, 30, and 60 min after release. (B) Two-dimensionl gel analysis of replication intermediates at the genomic origin ARS607, based on genomic DNA prepared from wild-type and GAL∷orc2-1 OFF cells released from α-factor into HU for 60 min. PstI–ClaI-digested genomic DNA was probed as described in Materials and Methods. (C,D) Wild-type (GA-1535), rad53 (GA-1499), and GAL1UAS∷orc2-1 (GA-1780) cells were synchronized by α-factor in YPAG at 30°C. After depletion of orc2-1p during α-factor block (A), cells were released into YPAD + 0.2 M HU, and aliquots were taken for spindle elongation analysis and FACS (D) as in Figure 1C–E. At 4–5 h, rad53 cells enter the next cell cycle.