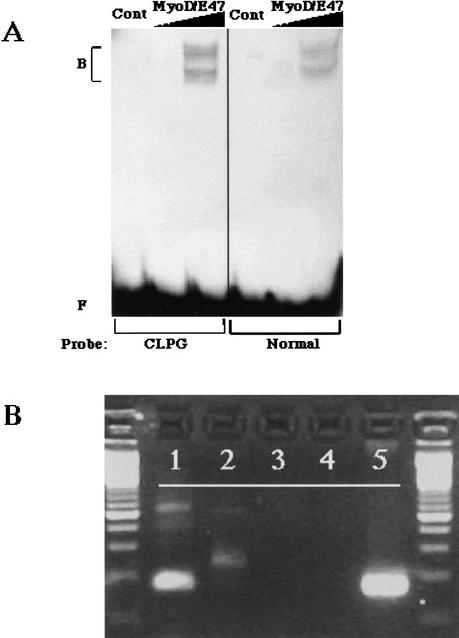
Figure 5.
Functional analysis of the region that encompasses the CLPG mutation. (A) An electrophoretic mobility shift assay using MyoD/E47 proteins and radiolabeled oligonucleotide probes representing the CLPG region. Probes were incubated either with no protein (Cont), 1 μL in vitro translated MyoD/E47, or 5 μL MyoD/E47, and the resulting complexes (B) were separated from free probe (F) by electrophoresis. MyoD/E47 forms two complexes with target DNA elements: the upper complex contains full-length proteins, and the lower complex contains a smaller translation product of E47 (Lemercier et al. 1998). (B) Expression of a transcript containing the CLPG mutation. RNA from fetal longissimus muscle was reverse transcribed with primer 21911 (primer sequence in Fig. 4) (lane 1) or 22051 5′- GCAAGGGTCTGTTTGGTCCTAA - 3′ (lane 2). Resulting cDNA was amplified with primer 21911 and a nested reverse primer, 22052 5′- GCTGGAGACGTGCAGCTCTAA - 3′. Control PCR with these primers utilized RNA from a mock reverse transcription to rule out DNA contamination (lane 3), no template negative control (lane 4), or ovine genomic DNA (lane 5).