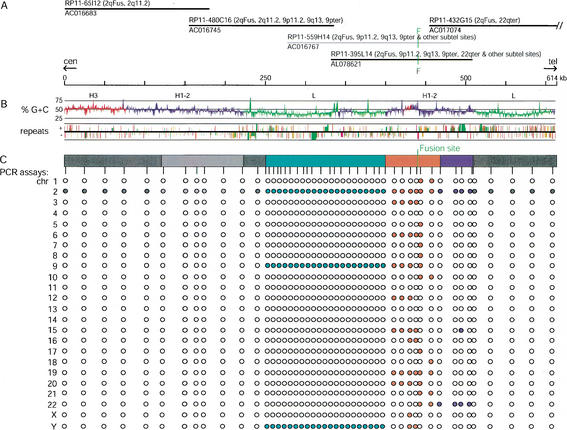
Figure 1.
Chromosomal distribution, GC content, and repeat content of 614-kb DNA sequence surrounding the 2q13–2q14.1 fusion site (2qFus). (A) Each black line indicates the sequence coverage of finished Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) clones assembled into the 2qFus contig on the basis of their 99.9%–100% identity in regions of overlap. BAC RP11–559H14 is unfinished (gray line); it overlaps RP11–480C16 and –395L15 with 99.7% identity, thereby confirming their overlap. Clone names are followed by chromosomal locations determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization; accession numbers are given below the lines. RP11–432G15 extends 35 kb off the right side of the map. Note that final GenBank entries for some of the BACs have been trimmed to remove overlap among clones exceeding 2 kb. The green vertical line marks the location of the inverted degenerate telomere repeats at the fusion site. The fusion site is immediately flanked by a telomere-associated repeat, TAR1, a repeat that is commonly found in close association with terminal telomere arrays and sometimes found near interstitial degenerate telomere repeats. (B) The G + C trace shows a graph of %GC content with window sizes of 500 bp for local content. Red, blue, and green regions represent H3, H1–H2, and L isochores, respectively, as defined by GESTALT using a 30-kb sliding window. The location, strand, age, and type of interspersed repetitive elements are shown in the third trace, also generated with GESTALT (Long Interspersed Elements [LINEs], green; Alus, red; Mammalian-wide Interspersed Repeats [MIRs], purple; all other repeats including retroviruses, Long Terminal Repeats [LTRs], Mammalian Apparent LTR-retrotransposons [MaLRs], etc., brown). The age of each element is indicated by the height of the feature; taller features represent evolutionarily more recent insertions. (C) Chromosomal distributions of sequence homologous to the 2qFus region as determined by PCR assays on a monochromosomal hybrid panel. Filled and open circles denote positive and negative PCR assays, respectively. The precise locations of the PCR assay are indicated by the vertical tick marks. The colored bar delineates regions with different chromosomal distributions. The light gray block within gray block indicates sequence duplicated within chromosome 2 (see Fig. 3).