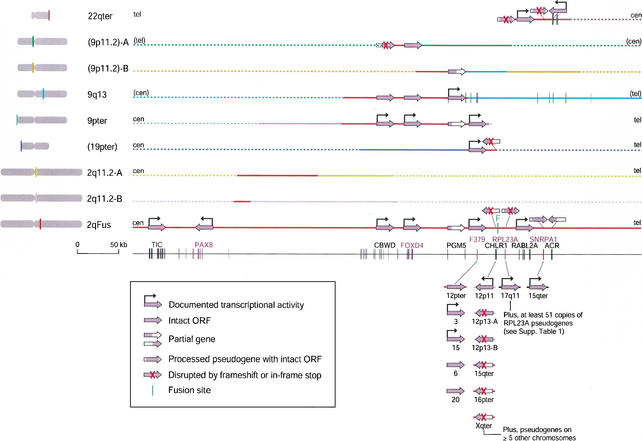
Figure 1.
Gene content of sequences at the 2q13–q14.1 fusion site and paralogous regions. Each line corresponds to sequence from a different chromosomal region. For the 68-kb region immediately surrounding the fusion site, only sequences with homology to genes are shown. Locations in parentheses are tentative (see below) and based on FISH, hybrid panel analysis, and the human genome assembly (Fan et al. 2002). The blocks on 9p11.2 may derive from 9q13. The large arrows indicate the state of each gene in each chromosomal location (e.g., full-length, partial, or disrupted ORF; see legend in figure) and point in the predicted direction of transcription relative to the genomic sequence. They are not drawn to scale. Bent black arrows indicate the genes for which transcriptional activity has been documented by us or others (see text). The exons of the 11 genes or pseudogenes identified in the 2qFus sequence are drawn to scale in the bottom line. As the 2qFus copies of PGM5 and ACR are partial genes, the exons for these genes are drawn to scale on the lines for 9q13 and 22qter, respectively. Details of sequence identity and chromosomal mapping data of homologous sequence blocks are provided in Fan et al. 2002. Solid lines indicate the extent of sequence coverage of available clones in the regions of interest as of March 1, 2002. Red solid lines indicate the regions with >95% average identity to 2qFus sequence. Red dotted lines indicate adjoining regions with no available sequence, but that were shown by PCR to be homologous to 2qFus (Fan et al. 2002). Different colors are used to indicate divergent sequence, with solid lines indicating the extent of contiguous sequence coverage, and dotted lines indicating either unavailable sequence or sequence in (non)overlapping clones that lack homology to any of the other segments shown. Orientations indicated in parentheses are tentative. In the bottom section, short lines extending from the gene arrows indicate flanking homology to 2qFus (red) or among each other (gray); the full extent of homology is not indicated. Gene arrows without protruding lines are sequences of PCR products (Mah et al. 2001). The GenBank accessions for sequences shown are 22qter (AC002055, AC002056), 9p11.2-A (AL512605), and 9p11.2-B (AL445925) (tentative; one or both may derive from 9q13, see Fan et al. 2002), 9q13 (AL161457, AL353608, AL353616), 9pter (AL356244, AL449043), 2q11.2-A (AC008268), 2q11.2-B (AC009238), 19pter (AL627309, tentative; Fan et al. 2002), 12pter (AC026369), 12p11 (AC008013), 12p13-A (AC009533), 12p13-B (AC092821), 15qter (AF282022/Z96310 and AC023024 (SNRPA1)), 16pter (Z84812), Xqter (AJ271736/M57752), 17q11 (AF001689), and 2qFus (AC016683, AC016745, AC017074, AL078621). All are finished sequence except AC092821.