Abstract
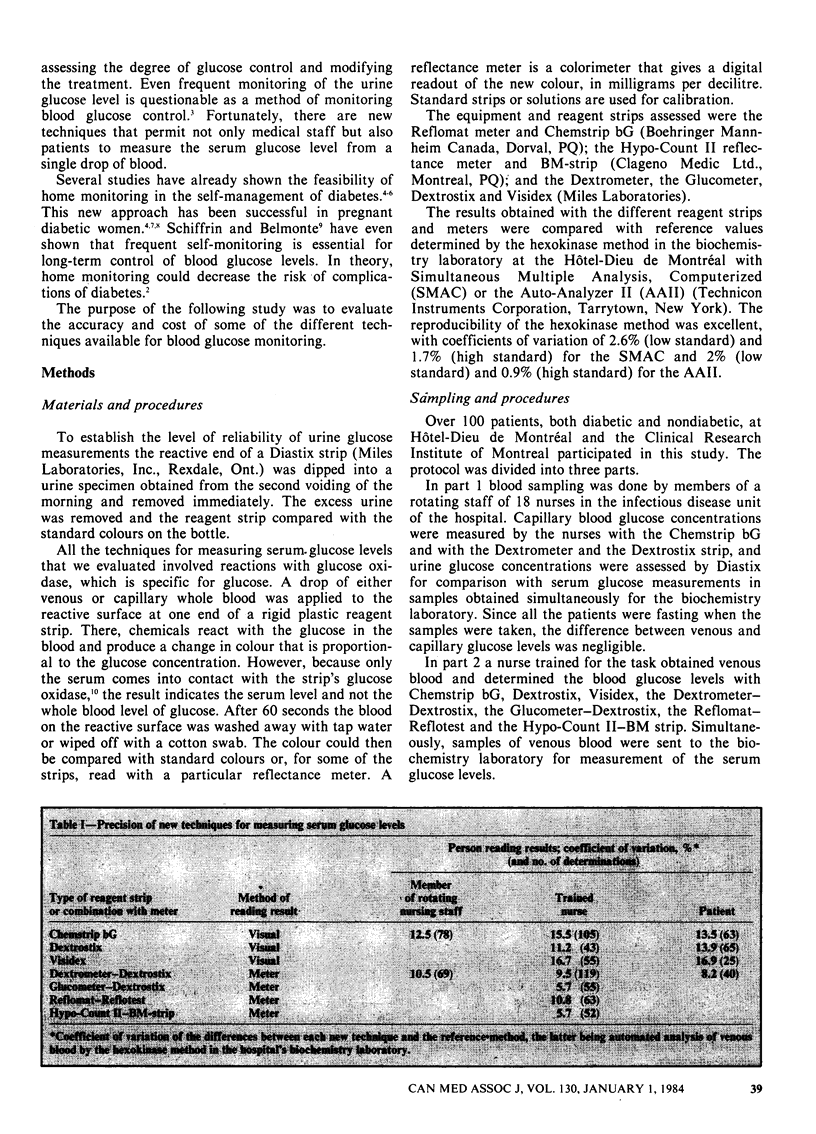
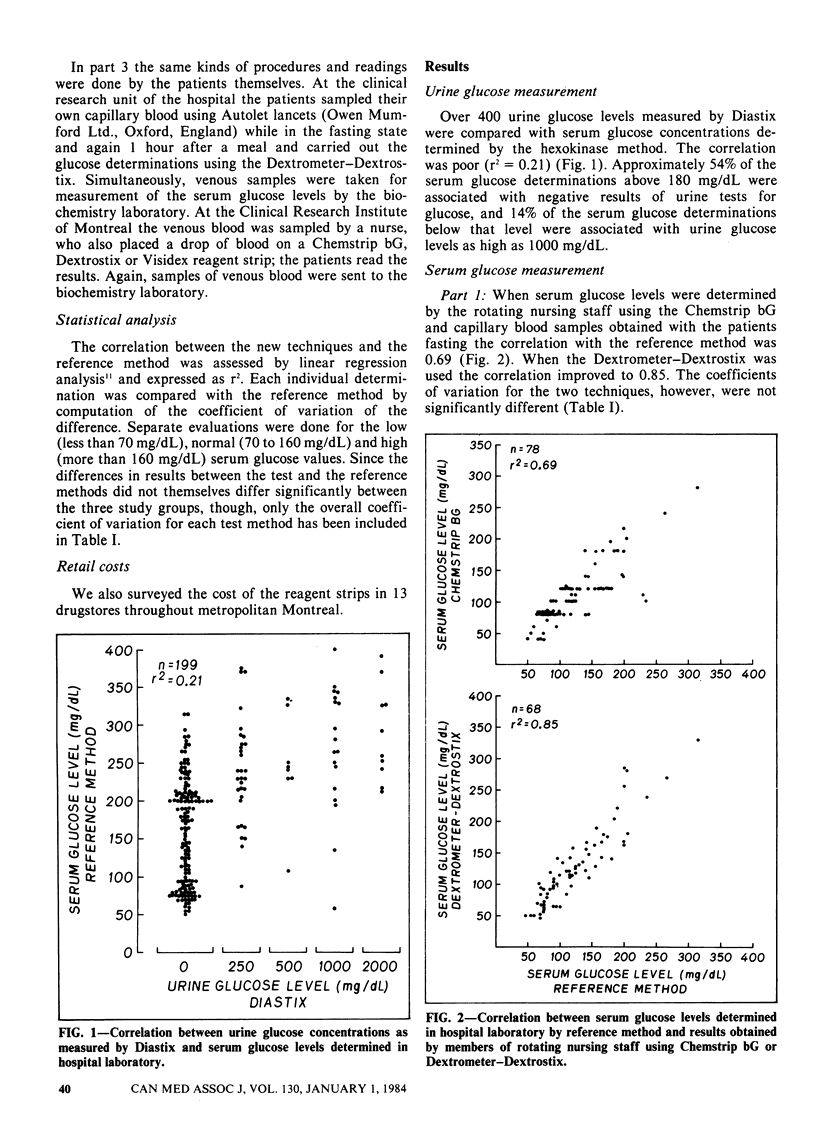
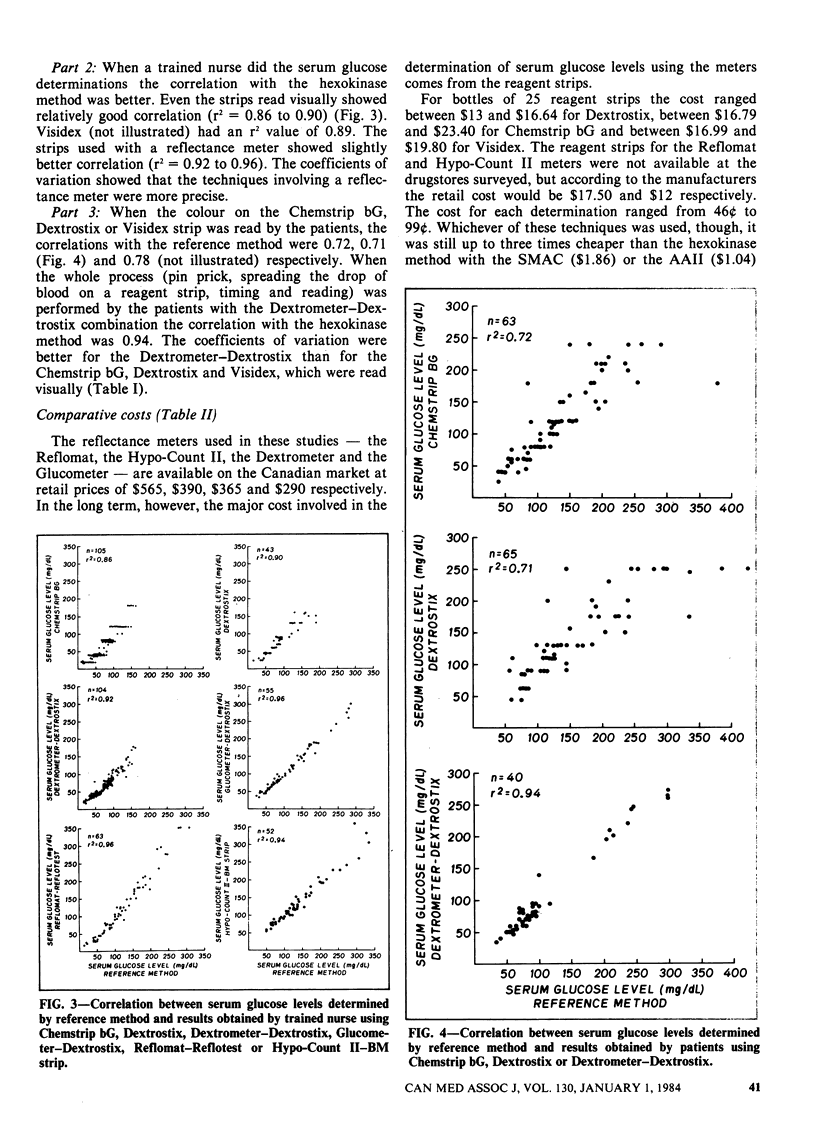
The poor correlation between serum and urine glucose measurements has led to the development of new techniques for monitoring the blood glucose level in diabetic patients. Either a nurse or the patient can perform these tests, which involve spreading a single drop of blood onto a reagent strip. A colour change that is proportional to the serum glucose level can be read visually or with a reflectance meter. Evaluated against simultaneous serum glucose levels determined by the hospital biochemistry laboratory, those of the new techniques employing reflectance meters all showed excellent correlation (r2 = 0.85 to 0.96). Reagent strips used without meters showed poorer correlation (r2 = 0.69 to 0.90). The instruction given to the patients and one nurse enabled them to obtain more accurate results with one of the meters than nurses not specially trained (r2 = 0.94 and 0.92 v. 0.85 respectively). The mean cost per glucose determination with the new techniques was 75, compared with +1.45 for the laboratory determinations done with automated equipment. It was concluded that the new techniques compared well with the reference method, particularly when reflectance meters were used, and that they were easily applied by the patient, as well as the medical staff, at a reasonable cost.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleyassine H., Gardiner R. J., Tonks D. B., Koch P. Glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes mellitus: correlations with fasting plasma glucose, serum lipids, and glycosuria. Diabetes Care. 1980 Jul-Aug;3(4):508–514. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.4.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements R. S., Jr, Keane N. A., Kirk K. A., Boshell B. R. Comparison of various methods for rapid glucose estimation. Diabetes Care. 1981 May-Jun;4(3):392–395. doi: 10.2337/diacare.4.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. H., Coburn P. C., Becker D., Drash A., Siminerio L. Measurement and modification of the accuracy of determinations of urine glucose concentration. Diabetes Care. 1980 Jul-Aug;3(4):535–536. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlén M., Strömblad G., Lithner F. Home monitoring of blood glucose without a photometer. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1980;238:157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Abarca G., Lopez D., Hamet M., Bourque M., Peyronnard J. M., Charron L., Larochelle P. Patient self-management of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Care. 1982 Sep-Oct;5(5):485–491. doi: 10.2337/diacare.5.5.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe-Davies S., Holman R. R., Phillips M., Turner R. C. Home blood sampling for plasma glucose assay in control of diabetes. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 26;2(6137):596–598. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6137.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. L., Forhan S. E., Skyler J. S., Peterson C. M. Comparison of methods for blood glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 1981 May-Jun;4(3):404–406. doi: 10.2337/diacare.4.3.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffrin A., Belmonte M. Multiple daily self-glucose monitoring: its essential role in long-term glucose control in insulin-dependent diabetic patients treated with pump and multiple subcutaneous injections. Diabetes Care. 1982 Sep-Oct;5(5):479–484. doi: 10.2337/diacare.5.5.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Judd S., Lowy C. Home monitoring of blood glucose: new approach to management of insulin-dependent diabetic patients in Great Britain. Diabetes Care. 1980 Jan-Feb;3(1):100–107. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford S., Clarke P., Paisey R., Hartog M., Allison S. P. Home blood-glucose measurements without reflectance meter. Lancet. 1980 Mar 22;1(8169):653–654. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


