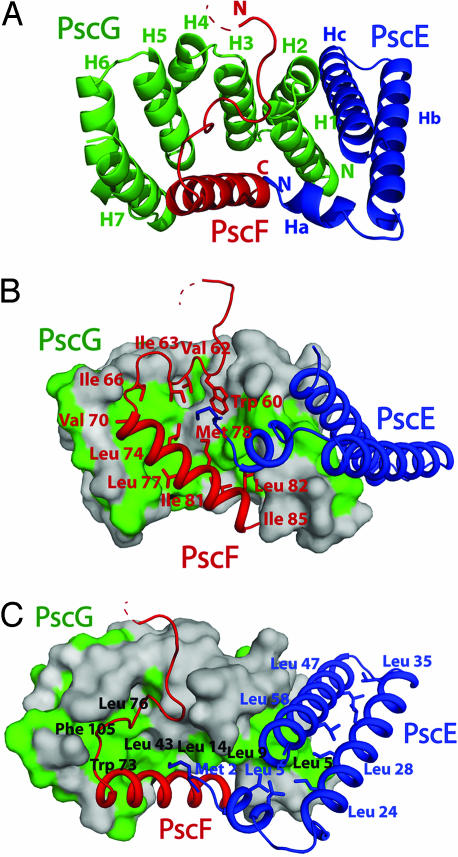
Fig. 2.
Formation of the PscE- PscF55–85-PscG heterotrimer involves different platforms of hydrophobic interactions. (A) The seven-helical TPR-like structure of PscG (green) stabilizes PscF55–85 (red) through its concave side and interacts with PscE (blue) by using its convex face. (B) Hydrophobic residues that line PscF (red) are stabilized within the concave face of PscG's nonpolar palm (green). Note that PscF residues 60–67, which form an extended coil, are also bound within the palm. (C) A second hydrophobic platform, formed by the outside face of PscG helices H1 and H2, is responsible for recognition of PscE. The antiparallel nature of PscE helices Hb and Hc is also maintained through hydrophobic interactions.