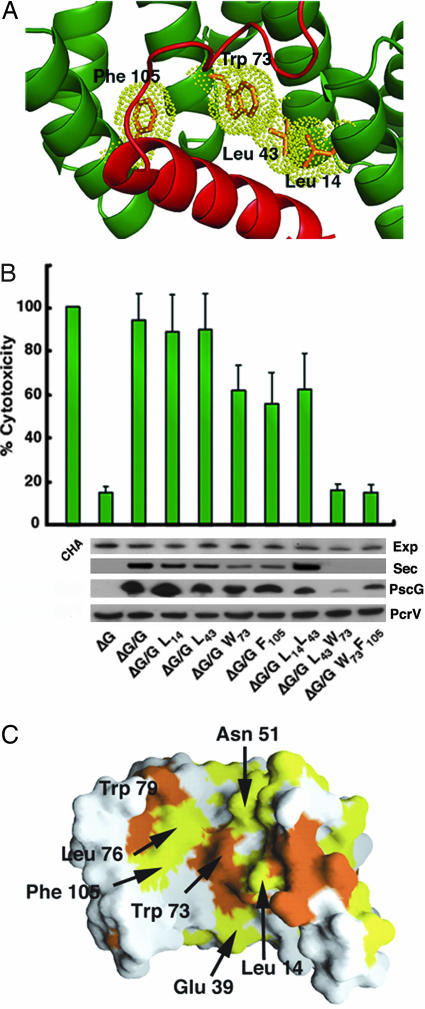
Fig. 4.
The PscG–PscF interaction platform is essential for T3SS viability. (A) Closeup of the PscG–PscF interaction region, showing the four hydrophobic residues that were mutated to Ser in this study. (B) Analysis of the effect of PscG mutations on cytotoxicity of the CHA P. aeruginosa isolate, from which pscG was chromosomally deleted. Strains expressing mutants PscG L43S/W73S and W73S/F105S can express (Exp), but not secrete (Sec), T3SS effector PopB and display only background cytotoxicity. A lower amount of PscG is detected in the cytoplasm of the double-mutant strains, whereas the levels of PcrV, an unrelated T3SS effector, are maintained. (C) Mapping of PscG residues that are identical (yellow) and similar (orange) within different bacterial species, revealing a highly conserved interface.