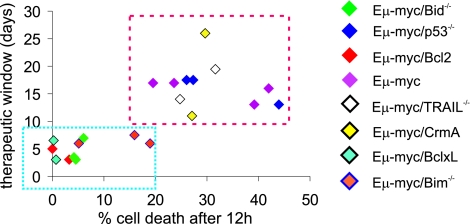
Fig. 6.
Apoptotic sensitivity to vorinostat in vivo correlates with therapeutic outcome. Sensitivity of lymphomas in the IVA assay correlates with therapeutic outcome. Specific cell death [(percent cell death after 12 h of vorinostat) − (percent cell death at 0 h)] was plotted against the therapeutic window [(median survival vorinostat cohort) − (median survival control cohort)]. Bcl-2- and Bcl-XL-overexpressing Bid−/− and Bim−/− lymphomas show low in vivo sensitivity to vorinostat, reduced responsiveness in therapy experiments, and form a “resistance” cluster (blue box). Eμ-myc, Eμ-myc/p53−/−, Eμ-myc/TRAIL−/−, and Eμ-myc/CrmA lymphomas were sensitive to vorinostat in vivo and formed a sensitive cluster (red box). The color of the diamonds corresponds to different genotypes, as outlined to the right. Statistical analysis: Mean specific cell death-resistant cluster = 5.9%; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.3–10.6%. Mean specific cell death in sensitive cluster = 30.4%; 95% CI = 25.1–35.8; P < 0.0001. Mean therapeutic window resistant cluster = 5.1 days; 95% CI = 3.8–6.3. Mean therapeutic window sensitive cluster = 16.5 days; 95% CI = 13.8–19.2; P < 0.0001.