Figure 2.
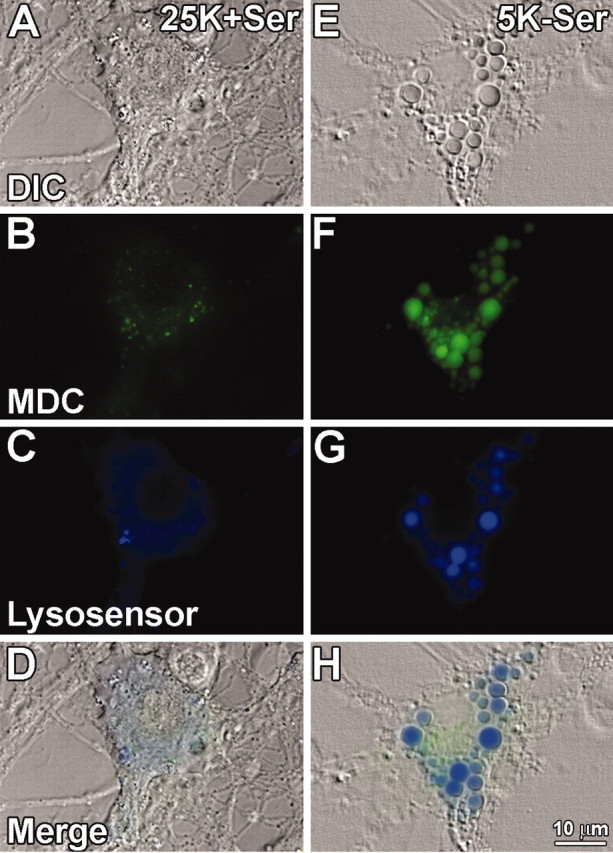
Autophagic and lysosomal markers stain vacuoles that form during Purkinje neuron degeneration. Purkinje neurons maintained in either control (25K+Ser) or trophic factor withdrawal (5K-Ser) media for 24 hr were stained with the autophagic marker MDC (green), and lysosensor blue, a pH-sensitive dye that fluoresces blue in acidic environments. Live cell imaging of control (A-D) and trophic factor-deprived (E-H) Purkinje neurons was performed. A, E, Bright-field images of cells identified as Purkinje neurons based on their morphology, characterized by a large cytoplasm (compared with granule neurons) and extensive neuronal processes. B, F, MDC staining demonstrating increases in autophagosomes in Purkinje neurons after trophic factor withdrawal. C, G, Lysosensor blue staining reveals acidic organelles (i.e., lysosomes) and demonstrates a marked increase in the size of lysosomes in Purkinje neurons after withdrawal of trophic factors. D, H, All three fields merged, demonstrating colabeling of some cytoplasmic vacuoles with both MDC and lysosensor blue indicative of autophagolysosomal fusion.
