Figure 5.
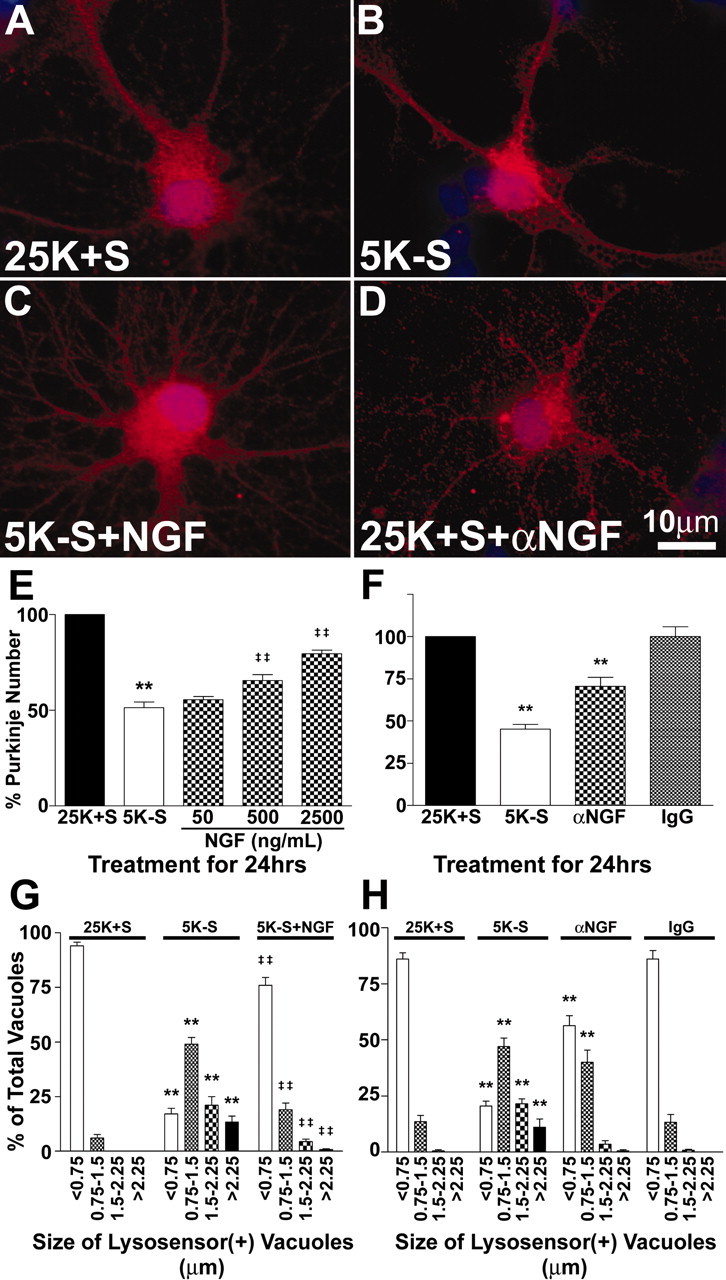
The neurotrophin NGF blocks the loss and the increased vacuolation of Purkinje neurons. A-D, Purkinje neurons maintained in various conditions were fixed and stained with antibodies to calbindin-D28k (a specific marker of Purkinje neurons; red) and the nuclear dye DAPI (blue). Images shown are representative of the effects of the various treatments. Purkinje neurons were maintained in control medium (A, 25K+S), trophic factor withdrawal medium (B, 5K-S), trophic factor withdrawal medium with 2500 ng/ml NGF (C, 5K-S+NGF), and control medium with 2 μg/ml NGF-neutralizing antibodies (D, 25K+S+αNGF) for 24 hr. E, Quantitation of the effects of NGF on Purkinje neuron numbers demonstrates that NGF partially rescues Purkinje neurons from death in a concentration-dependent manner after 24 hr of trophic factor withdrawal, compared with healthy controls. F, Quantitation of the effects of NGF-neutralizing antibodies on Purkinje neuron numbers demonstrates that depleting NGF from control media results in a loss of Purkinje neurons, whereas control antibodies had no effect on Purkinje survival. Numbers are mean ± SEM values of at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. G, H, The effects of the various treatments on vacuole size were quantified by measuring the diameters of all visible lysosensor blue-positive vacuoles in 6-12 Purkinje neurons per treatment condition in at least three independent experiments. Usually, the total number of vacuoles measured per condition was between 100 and 200. The size distribution was graphed as a percentage of total vacuoles that were within the indicated size ranges. G, A high concentration of NGF (2500 ng/ml) significantly decreased the autophagic vacuolation of Purkinje neurons induced by 24 hr of trophic factor withdrawal. H, NGF-neutralizing antibodies significantly increased the vacuolation of Purkinje neurons in control media. E-H, **, *Significant difference from 25K+S (**p < 0.01; *p < 0.05). ‡‡,‡Significant difference from 5K-S (‡‡p < 0.01; ‡p < 0.05).
