Figure 1.
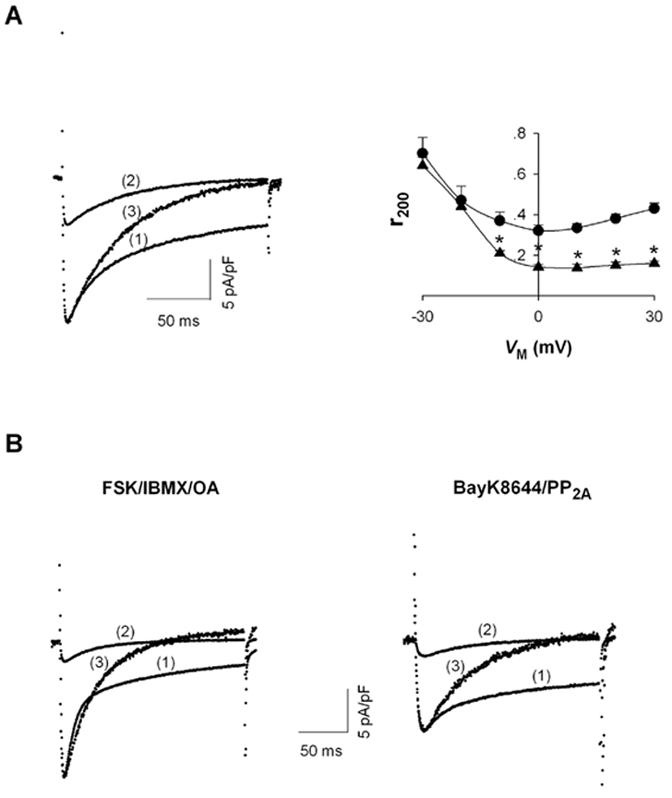
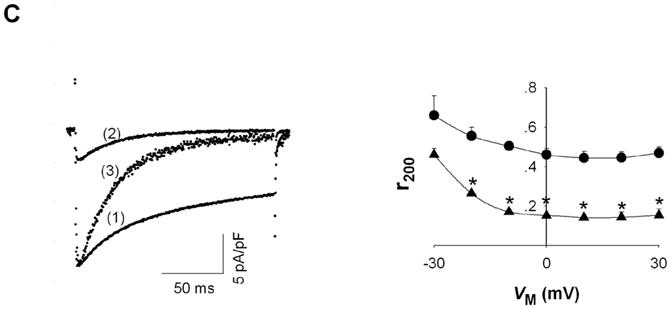
Effect of [Mg2+]p on L-type Ca2+ channel currents. A, ICa recorded during depolarizations to 0 mV in rat ventricular myocytes voltage-clamped with patch electrodes containing (1) 0.2 mM [Mg2+]p and (2) 1.8 mM [Mg2+]p. Trace (3) is ICa with 1.8 mM [Mg2+]p normalized to the amplitude of ICa with 0.2 mM [Mg2+]p (left). The fraction of peak ICa remaining at the end of 200-ms depolarizations (r200) with 0.2 mM (● , n=6) and 1.8 mM [Mg2+]p (▲ , n=5) at different test potentials (VM) (right). Significant changes of r200 between 0.2 mM [Mg2+]p and 1.8 mM [Mg2+]p are indicated by asterisks. B, tracings of ICa, as in part A, except with the addition of the indicated compounds. C, IBa recorded during depolarizations to 0 mV. Current traces (1) - (3) are indicated as in Part A (left); r200 for IBa was measured with 0.2 mM (● , n=7) and 1.8 mM [Mg2+]p (▲ , n=6) and plotted versus test potential (right).
