Figure 1.
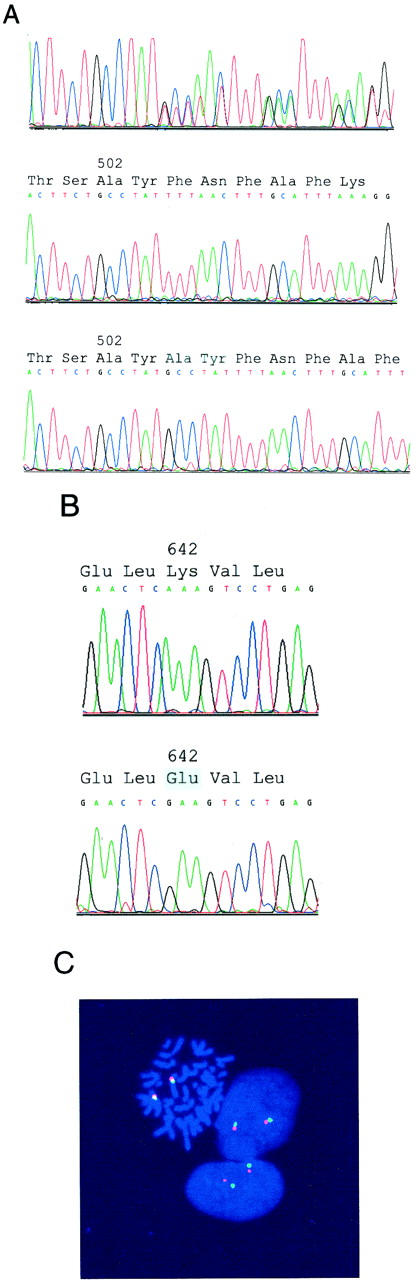
Genomic evaluations of KIT by sequencing (A and B) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (C). A: Sequence analysis of total genomic DNA demonstrates a heterozygous exon 9 6-bp insertion/duplication in a GIST (top). Sequence analysis of cloned PCR products, from the same GIST as shown at top, demonstrates the wild-type (middle) and mutant (bottom) alleles. B: Sequence analysis of total genomic DNA demonstrates a homozygous exon 13 A>G missense mutation. The GIST sequence is at bottom, and the wild-type sequence, obtained from adjacent nonneoplastic tissue, is at top. C: Fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrates nondeleted KIT, in the same GIST as in B, consistent with loss of the chromosome 4 homolog containing the wild-type KIT allele and duplication of the chromosome 4 homolog containing the mutant KIT allele. FITC signals (green) identify the KIT loci at chromosome band 4q12, and rhodamine signals (red) identify the chromosome 4 pericentromeric region.
