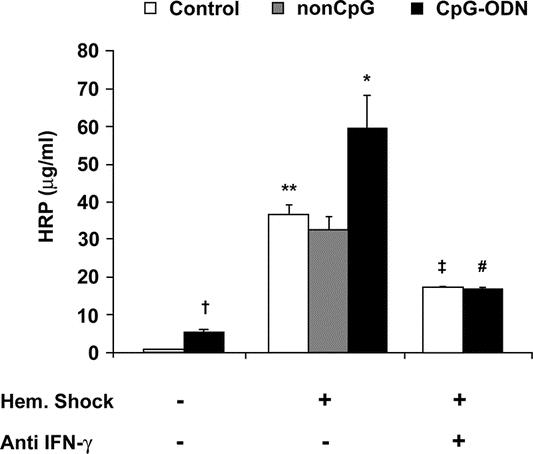
FIGURE 3. Preexposure to CpG-ODN followed by hemorrhagic shock enhanced intestinal permeability for horseradish peroxidase (HRP) via an IFN-γ-dependent route. Exposure to CpG-ODN increased permeability for HRP (5.5 ± 0.5 μg/mL, †P < 0.01) compared with control rats (1.0 ± 0.1 μg/mL). Hemorrhagic shock caused a substantial leakage of HRP (36 ± 3 μg/mL, **P < 0.01). Preexposure to CpG-ODN followed by hemorrhagic shock strongly aggravated intestinal permeability for HRP (60 ± 11 μg/mL, *P < 0.05). Administration of anti IFN-γ markedly reduced permeability for HRP in both control (‡P < 0.05) and CpG-ODN-treated rats (#P < 0.01) subjected to hemorrhagic shock: **,†compared with control; *compared with control hemorrhagic shock; #compared with CpG-ODN shock; ‡compared with control hemorrhagic shock.
