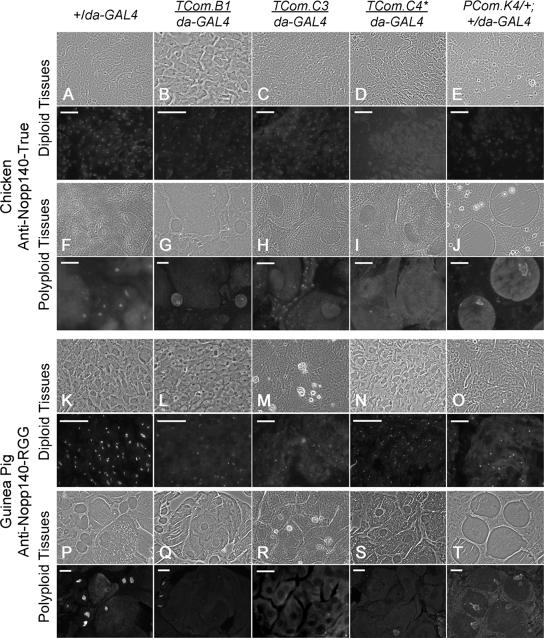
Figure 4.
Immunofluorescence microscopy used the isoform-specific antibodies characterized in Figure 3 to detect endogenous Nopp140-True (A–J) and Nopp140-RGG (K–T) in control (+/da-GAL4) larvae or larvae and pupae heterozygous for an RNAi-expressing transgene and da-GAL4. In each set of figures, the immunofluorescence image is directly below the corresponding phase-contrast image. (A–E) Larval diploid imaginal (wing or leg) disk cells were probed with anti-Nopp140-True. Nucleolar staining was clearly evident in +/da-GAL4 control cells, weaker in TCom.B1/da-GAL4, TCom.C3/da-GAL4, and PCom.K4/+; +/da-GAL4 discs, but nearly absent in TCom.C4/daGAL4 disk cells. (F–J) Larval polyploid (midgut, Malpighian tubule, or salivary gland) cells stained with anti-Nopp140-True. Nucleolar staining was similar in the +/da-GAL4, TCom.B1/da-GAL4, and PCom.K4/+; +/da-GAL4 polyploid cells, but absent in the TCom.C3/da-GAL4 and TCom.C4/da-GAL4 polyploid cells. Notice that diploid imaginal island cells in the TCom.C3/da-GAL4 midgut retained nucleolar staining. (K–O) Larval imaginal diploid cells (K, L, N, and O) or pupal diploid cells (M) were probed with anti-Nopp140-RGG. Nucleoli in control +/da-GAL4 cells stained brightly, whereas nucleoli in the four RNAi-expressing lines were less intensely labeled. Most importantly, nucleoli in patches of cells failed to stain. (P–T) Larval polyploid cells (P, Q, S, and T) and pupal polyploid cells (R) were probed with anti-Nopp140-RGG. Nucleoli in control +/da-GAL4 cells labeled brightly, whereas nucleoli in polyploid cells stained weakly (PCom.K4/+; +/da-GAL4) or not at all. * TCom.C4 has two RNAi-expressing transgenes, one on the second chromosome and one on the third chromosome. Bars, 100 μm.