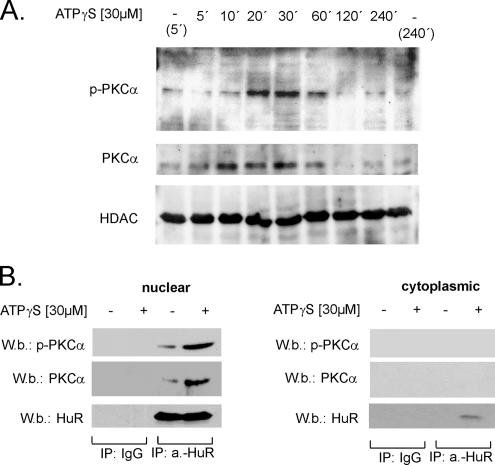
Figure 4.
Nuclear translocation of PKCα by ATPγS is accompanied with an increased binding of PKCα to nuclear HuR. (A) Time course of PKCα translocation to the nucleus by ATPγS. Quiescent hMC were treated with either vehicle (−) or with 30 μM ATPγS and lysed after the indicated times. Nuclear extracts (50 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and successively immunoblotted with a phosphorylation-independent (PKCα) and a phospho-specific (p-PKCα) PKCα antibody. To ascertain equal protein contents within the nuclear fractions, the blots were stripped and reprobed with an HDAC4-specific antibody. The Western blots shown are representative of three independent experiments giving similar results. (B) IP-phospho-PKCα (P-PKCα) and PKCα (PKCα) levels after an overnight incubation with 2 μg of either anti-HuR antibody (a.-HuR) or an irrelevant IgG isotype antibody (IgG) used as a negative control. For IP, a total protein amount (500 μg) of either nuclear (left) or cytoplasmic extract (right) and derived from either untreated (−) or ATP-treated hMC (+) was taken, and immunocomplexes were separated by Sepharose G as described in Materials and Methods. Equal amounts of immunoprecipitated HuR were ascertained by stripping the blot and reincubating with the anti-HuR antibody also used for IP. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments giving similar results.