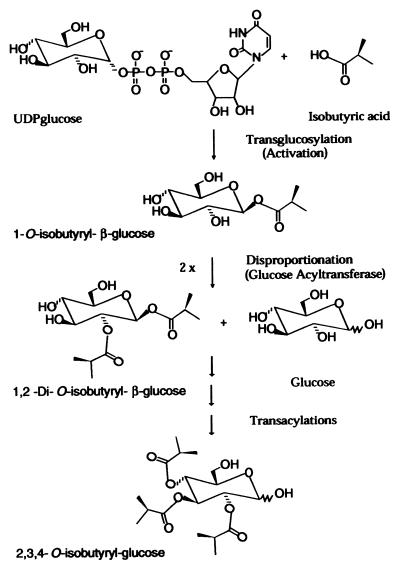
Figure 1.
Acylglucose biosynthetic pathway. Fatty acids are activated by means of UDPglucose-dependent transglucosylation to form the high-energy acyl donor molecule, 1-O-acyl-β-glucose. Two equivalents of the activated 1-O-acyl-β-glucose intermediate then undergo enzyme-catalyzed disproportionation to form 1,2-substituted diacylglucose and glucose. In this figure, isobutyrate represents the acyl group; however, branched and straight short (C4–C5) to medium (C10–C12) chain fatty acids are used in acylglucose biosynthesis and are activated by chain length-specific UDPglucose:fatty acid transglucosylases.