Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a multifactorial systemic disease in which genetic, immunologic, hormonal, and environmental factors may contribute to disease pathogenesis. Bacterial products (eg, bacterial lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) induce a lupuslike disease in normal mice and trigger an early and accelerated form of lupus nephritis in NZB/W mice. To investigate whether the mechanism by which LPS accelerates nephritis in the NZB/W mice involves interference with processing of immune complexes (IC), we administered LPS to NZB/W mice for 5 weeks and probed the kinetics of removal, liver uptake, and organ localization of a subsaturating dose of radiolabeled IC (2.5 mg of bovine serum albumin-antibovine serum albumin). Control NZB/W mice received vehicle (saline) alone. In NZB/W exposed to LPS, features of polyclonal B-cell activation (PBA) were enhanced, anti-DNA antibodies were raised, and a proliferative glomerulonephritis developed that was associated with renal insufficiency and substantial proteinuria. This LPS-accelerated nephritis could not be attributed to altered complement concentration, to altered blood cell carrier function, to delayed removal of pathogenic (large-sized) ICs from the circulation, to impaired liver uptake of ICs, or to enhanced localization of ICs in kidney. The findings indicate that transformation of nephritis is probably the result of LPS-induced PBA, that defective processing of pathogenic IC is not a contributory factor to nephritis, and that mechanisms other than passive renal localization of circulating ICs must be operative.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S., Kramer S. B., Radin A., Holzman R. Salmonella bacteremia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eight-year experience at a municipal hospital. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jan;28(1):75–79. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. The switch from IgM to IgG secretion in single mitogen-stimulated B-cell clones. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1744–1754. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Melchers F., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mouse lymphocytes. Lipid A as the mitogenic part of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):943–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockow B., Mannik M. Clearance and tissue uptake of immune complexes in complement-depleted and control mice. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
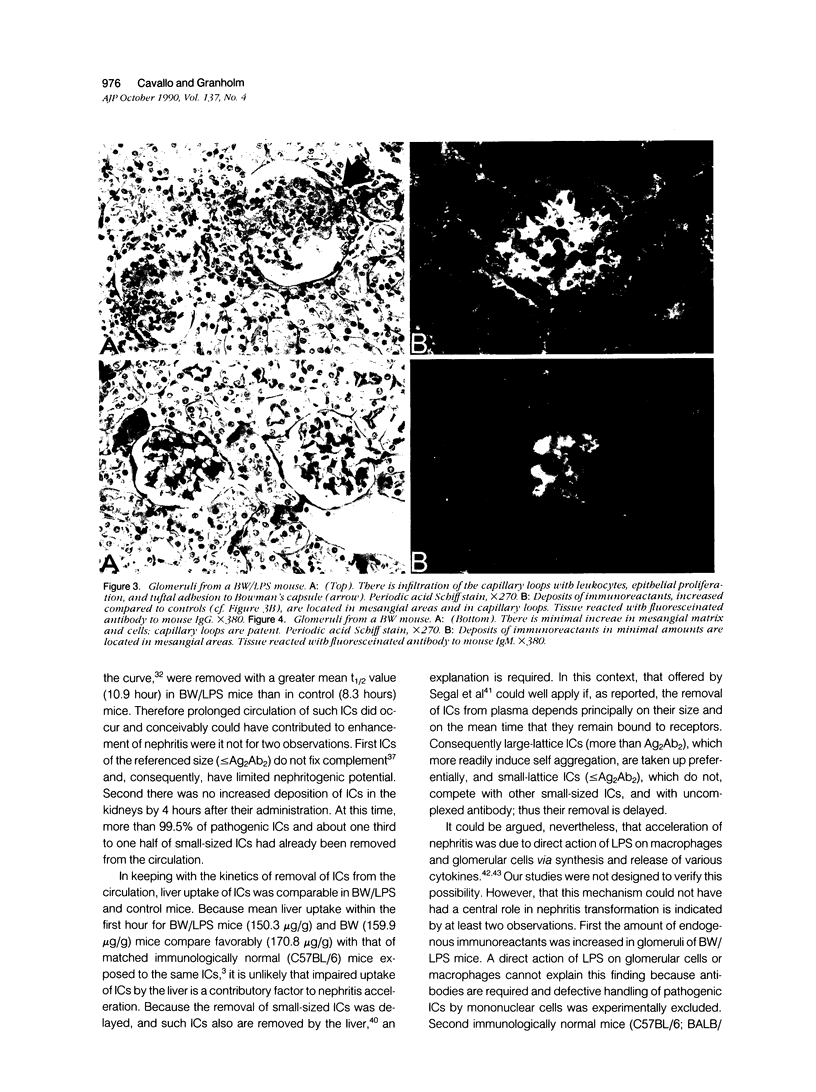
- Cavallo T., Cameron W. R., Lapenas D. Immunopathology of early and clinically silent lupus nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 1977 Apr;87(1):1–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo T., Goldman M., Graves K., Lambert P. H. Altered glomerular permeability in the early phase of immune complex nephritis. Kidney Int. 1983 Nov;24(5):632–637. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo T., Goldman M., Lambert P. H. Animal model of human disease. Proliferative glomerulonephritis associated with polyclonal B-cell activation. Am J Pathol. 1984 Feb;114(2):346–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo T., Granholm N. A. Repeated exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide interferes with disposal of pathogenic immune complexes in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. K., Cavallo T. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Localization of early components of complement in glomerular deposits. Am J Pathol. 1976 Aug;84(2):283–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Plotz P. H. Studies of reticuloendothelial function in the mouse with model immune complexes. I. Serum clearance and tissue uptake in normal C3H mice. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1594–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié G. J., Mignon-Conté M. A., Lulé J., Gayral-Ta Minh M., Haas S., Bauriaud R., Conté J. J. Immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice infected with Escherichia coli. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Oct;42(1):77–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Lawley T. J., Hamburger M. I., Brown E. J. NIH Conference: Immunoglobulin G Fc receptor-mediated clearance in autoimmune diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Feb;98(2):206–218. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-2-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granholm N. A., Cavallo T. Defective disposal of immune complexes and polyclonal B cell activation persist long after exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide in mice. Lab Invest. 1989 Nov;61(5):504–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Mannik M. Saturation of the reticuloendothelial system with soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1939–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Striker G. E., Mannik M. The disappearance kinetics and glomerular deposition of small-latticed soluble immune complexes. Immunology. 1982 Nov;47(3):407–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Striker G. E., Mannik M. The disappearance kinetics and glomerular deposition of small-latticed soluble immune complexes. Immunology. 1982 Nov;47(3):407–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L., Slack J. H., Amundson C., Izui S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Induction of murine autoimmune disease by chronic polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):874–883. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Eisenberg R. A., Dixon F. J. Subclass-restricted IgG polyclonal antibody production in mice injected with lipid A-rich lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):324–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Determination of anti-DNA antibodies by a modified 125I-labelled DNA-binding test. Elimination of non-specific binding of DNA to non-immunoglobulin basic proteins by using an anionic detergent. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):425–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for a local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):428–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Presence of heparan sulfate in the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1303–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Cavallo T. An ultrastructural study of the glomerular slit diaphragm in New Zealand black/white mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Bursten S. L., Gemsa D., Bessler W., Resch K., Ryan J. L. Activation of glomerular mesangial cells by gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):472–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Carlson J., Cataldo J., Ucci A., Migliorini P., Pankewycz O. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Saluk P. H., Nussenzweig V. Complement-dependent release of immune complexes from the lymphocyte membrane. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):495–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Steinberg A. D., Green I., Nussenzweig V. Complement-dependent alterations in the handling of immune complexes by NZB/W mice. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1166–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell G. P., Pirotzky E., Erard D., Desmottes R. M., Bidault J., Damais C., Benveniste J. Paf-acether (platelet-activating factor) and interleukin-1-like cytokine production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated glomeruli. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Mar;46(3):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Leinonen M., Saikku P., Mäkelä P. H. The genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia: resemblance to the lipopolysaccharide of enteric bacteria. Science. 1983 Jun 17;220(4603):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6344216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce A. J. Methods used for the analysis of proteins in the urine. Nephron. 1974;13(1):93–104. doi: 10.1159/000180371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Taylor R. P. Physiological and pathological aspects of circulating immune complexes. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):993–1003. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Titus J. A., Dower S. K. The FcR-mediated endocytosis of model immune complexes by cells from the P388D1 mouse macrophage line. II. The role of ligand-induced self-aggregation in promoting internalization. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinson E., Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., van der Loo W., Fernandez C. Characterization of the IgG response induced by polyclonal B cell activators. Immunol Rev. 1982;67:73–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb01056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Hirose S. Solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes: a new function of complement as a regulator of immune reactions. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:134–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triolo G., Giardina E., Scarantino G., Seddio G., Cardella F., Meli F., Bompiani G. Cross-reactivity of anti-ssDNA antibodies with heparan sulfate in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):718–722. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]