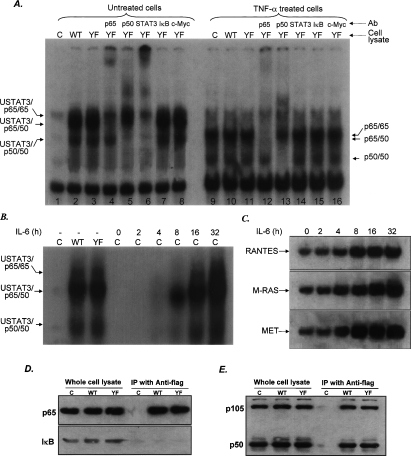
Figure 2.
U-STAT3 binds to U-NFκB. (A) DNA-binding assays. The EMSAs shown were performed with whole-cell extracts. Assays with nuclear extracts (not shown) gave similar results. (C) hTERT-HME1 control cells. A DNA fragment of the human RANTES promoter, bases −58 to −29, containing a κB element, was used as the labeled probe. (Lanes 1–8) Extracts of untreated cells: control cells (lane 1), WT cells (lane 2), YF cells (lane 3), and supershifts obtained with extracts of YF cells following addition of antibodies directed against p65, p50, STAT3, IκB, or c-Myc (lanes 4–8). (Lanes 9–16) Same as lanes 1–8 except that the extracts are from cells treated with TNF-α for 4 h. (B) EMSAs. Whole-cell extracts were made from hTERT-HME1 cells, untreated or treated with IL-6. The probe was same as in A. (C) Northern analysis. Total RNAs (20 μg per lane) from hTERT-HME1 cells untreated or treated with IL-6 were analyzed by the Northern method. (D,E) STAT3 binds to p65, p50, and p105 but not to IκB. STAT3 was immunoprecipitated from whole-cell extracts of the cells shown in Figure 1A by using anti-Flag M2 beads. Western analyses were performed to detect p65, p50, and IκB.