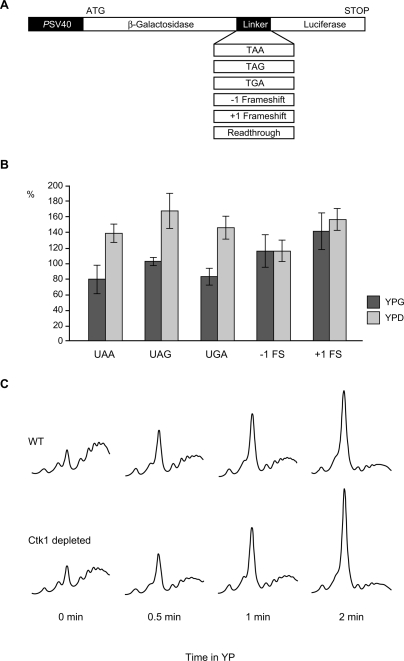
Figure 4.
Ctk1 plays a role in decoding fidelity in vivo. (A) Schematic showing the dual reporter system used for determination of miscoding frequency in B. (B) Loss of Ctk1 function leads to an increase in the frequency of miscoding. Cells depleted for Ctk1 by growth in glucose-containing medium (YPD) show an increase in the frequency of miscoding with all three stop codons (UAA, UAG, and UGA) compared with cells expressing Ctk1 (YPG), whereas an increased rate of frameshift events does not occur (−1 FS and +1 FS). (C) Depletion of Ctk1 leads to a slightly faster polysome run-off after inhibition of translation initiation. Wild-type (WT) and GAL1∷CTK1-TAP cells grown in YPD were shifted to glucose-lacking medium (YP) to inhibit translation initiation for the indicated time points and polysome profiles analyzed.