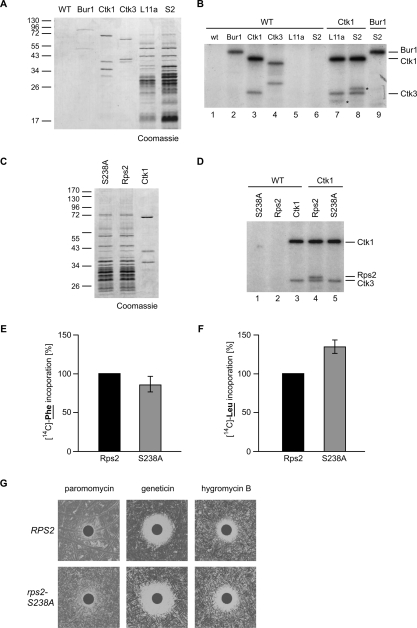
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of Rps2 on Ser 238 by Ctk1 is needed for translational accuracy. (A) Complexes purified for the in vitro kinase assay shown in B. The CTDK-I complex was purified by a TAP tag on Ctk1 or Ctk3, the Bur1–Bur2 complex via TAP-tagged Bur1, and ribosomes were purified via TAP-tagged Rpl11a (L11a) or Rps2 (S2). A nontagged wild-type (WT) strain served as negative control. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie. The left lane shows a molecular weight marker. (B) Ctk1 phosphorylates Rps2 in vitro. The protein complexes indicated by the component that was TAP-tagged for the purification were used in in vitro kinase assays. After incubation with radioactively labeled ATP, proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, and phosphorylated proteins were visualized by autoradiography. An eluate of a nontagged wild-type strain served as negative control. Incubation of the control eluate alone (WT; lane 1) or of Rpl11a (L11) or Rps2 (S2) containing ribosomes with control eluate (lanes 5,6) did not give a radioactive signal. Incubation of Bur1, Ctk1, and Ctk3 with the control eluate (WT; lanes 2–4) gave signals for (auto)phosphorylated Bur1, Ctk1, and Ctk3. (Lane 7) Incubation of Ckt1 with Rpl11a-purified ribosomes yields an additional phosphorylated protein (indicated by a star). (Lane 8) This band shifts up when CBP-tagged Rps2-containing ribosomes (S2) are incubated with Ctk1, identifying Rps2 as the phosphorylated product (Rps2-TAP indicated by a star). (Lane 9) Bur1, used as a control kinase, does not phosphorylate Rps2. (C) Coomassie staining of purified ribosomes containing Rps2 or Rps2–S238A and CTDK-I complex used for the in vitro kinase assays shown in D. (D) Ctk1 phosphorylates Rps2 on S238. (Lane 4) Ctk1 phosphorylates itself, Ctk3, and Rps2. (Lane 5) In contrast, when ribosomes containing Rps2–S238A–CBP are used as substrate, no phosphorylation of Rps2 can be observed. (E,F) rps2-S238A extracts show a minor decrease in translation elongation and an increase in miscoding events. Experiments were performed as described in Figure 3B. (G) rps2-S238A cells are sensitive to drugs that impair translation elongation.