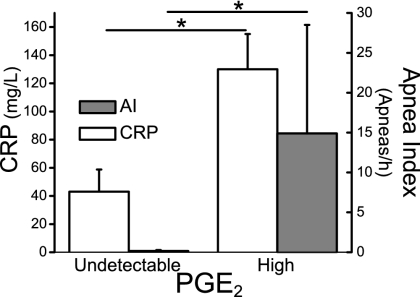
Fig. 5.
PGE2 in CSF is correlated to apnea index in neonates. CSF was collected from infants in the neonatal intensive care unit who had clinical indications for lumbar puncture (n = 12, mean postnatal age 16 ± 4 d; mean gestational age 32 ± 2 week). Infants then underwent a cardiorespiratory recording (duration 9.2 ± 2.4 h). PGE2 concentrations in the CSF were analyzed using a standardized enzyme immunoassay (EIA) protocol and correlated to the infectious marker CRP and apnea index (number of apneas per h). Central PGE2 concentrations were positively correlated to the CRP levels in blood (P = 0.01). Moreover, a striking association was observed between central PGE2 concentrations and apnea index (P < 0.05). Here, we distinguish between undetectable levels of PGE2 (0 ± 0 pg/ml) compared with high levels of PGE2 (52 ± 22 pg/ml). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.