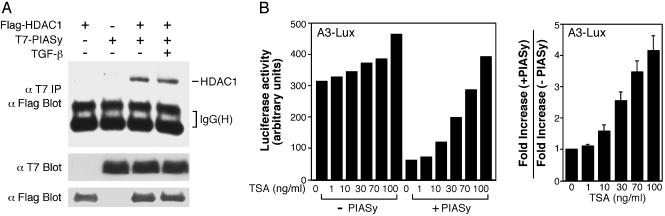
Fig. 6.
PIASy can inhibit Smad-mediated transcriptional activation in an HDAC-dependent manner. (A) Interaction of PIASy and HDAC1. Flag-HDAC1, T7-PIASy, and TβRI (T204D) for TGF-β stimulation were cotransfected into COS cells and analyzed as indicated. (B) TSA can disrupt the inhibitory effect of PIASy. Mv1Lu/L17 cells were cotransfected with the A3-Lux reporter gene and FAST-1 in the absence or presence of 300 ng of PIASy DNA. Cells were treated with TGF-β and increasing amounts of TSA at the same time for 18–24 h and then were analyzed for luciferase activity. (Left) One representative experiment. (Right) Summary of several experiments. For each dose of TSA, the fold increase refers to the luciferase activity in the presence of TSA divided by the luciferase activity in the absence of TSA. The fold increase in the presence of cotransfected PIASy divided by the fold increase in the absence of PIASy then was calculated and plotted against each dose of TSA. This ratio in the absence of TSA is set as 1.