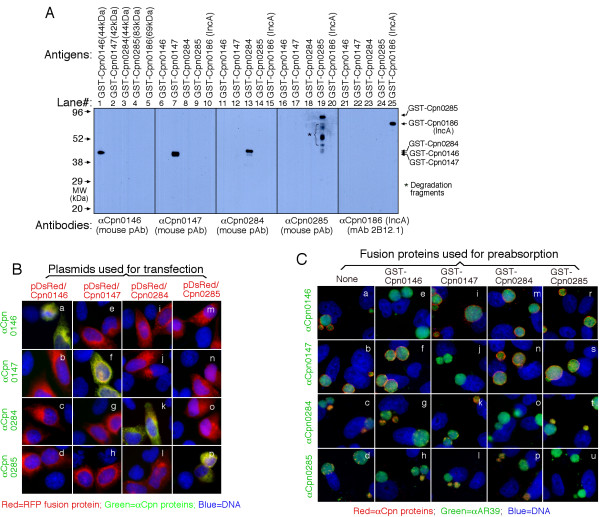
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the anti-Cpn fusion protein antibody binding specificities using three different methods. (A) Various GST-Cpn fusion proteins listed on top of the figure were resolved in SDS polyacrylamide gels and the protein bands were transferred onto membranes for Western blot detection with antibodies listed at the bottom of the figure. The molecular weight (MW) was listed in kDa on the left while the corresponding fusion protein bands detected were indicated on the right of the figure. Star * denotes degradation fragments of fusion proteins. Note that the antibodies only detected the corresponding fusion proteins without cross-reacting with unrelated fusion proteins under the current experimental conditions. In separate experiments, pre-absorption of the primary antibodies with corresponding but not unrelated fusion proteins blocked the antibody binding to fusion protein bands (data not shown). (B) HeLa cells transfected with the recombinant plasmids pDsRed-C1 monomer/Cpn0146 (panels a-d), /Cpn0147 (e-h), /Cpn0284 (i-l) and /Cpn0285 (m-p) were processed for immunostaining with various antibodies listed along the left of the figure (green) plus Hoechst (Blue). The Cpn proteins were expressed as RFP fusion proteins (red). Note that the antibodies only labeled the corresponding homologous gene-transfected cells (panels a, f, k & p; yellow) without cross-reacting with the unrelated gene-transfected cells. (C) The anti-Cpn0146, 0147, 0284 and 0285 antibodies were preabsorbed with or without the GST fusion proteins listed on top of the figure followed by immunostaining as described in Fig. 1A legend. Note that antibody staining was only blocked by pre-absorption with the corresponding homologous GST fusion proteins.