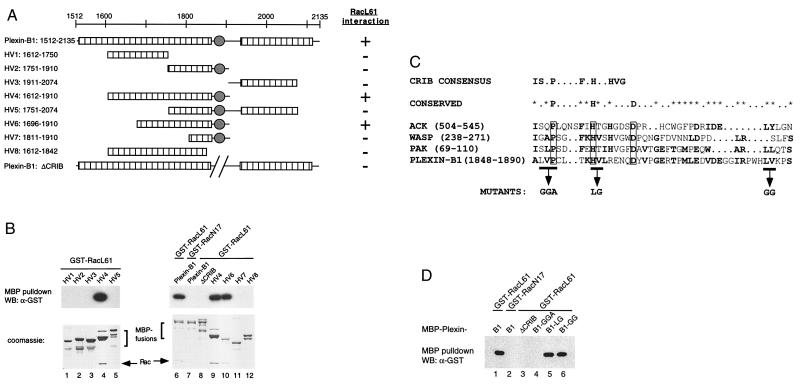
Figure 3.
(A) Mapping the Rac binding domain in plexin-B1. The intracellular domain of plexin-B1 (residues 1512–2135) contains two conserved regions as depicted by the hatched bars. The filled circle denotes the CRIB motif found in plexin-B1, which is not conserved in other members of the plexin family. The results of the in vitro interaction are summarized in the right column. (B) Interaction between RacL61 and deletion mutants of plexin-B1. Various MBP-plexin-B1 deletion proteins were expressed and purified from E. coli and used for in vitro interaction with GST-RacL61. The samples were stained with Coomassie (lower) or detected by α-GST WB (upper). (C) Sequence alignment of the CRIB domain of plexin-B1. The CRIB consensus defined by Burbelo et al. is shown (upper) (31). Residues conserved among ACK, WASP, PAK, and plexin-B1 are shown (lower). The invariable P, H, and D are boxed whereas * denotes partially conserved residues. (D) Mutation in the CRIB motif disrupts interaction with plexin-B1. MBP-plexin-B1 fusion proteins, containing mutations in the CRIB domain as indicated, were expressed and purified from E. coli and used for in vitro interaction with GST-RacL61. The samples were analyzed by α-GST WB.